Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) are abnormal heartbeats originating in the atria, sometimes signaling underlying issues. Sinus Arrhythmia, a benign irregularity, showcases heart rate variations with breathing. PACs might need medical attention if frequent, while Sinus Arrhythmia, often harmless, seldom requires treatment. Understanding these heart rhythm variations is crucial for tailored management and overall heart health optimization.
What is PAC?
Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC) is a type of irregular heartbeat that originates in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. In PAC, the heart’s regular rhythm is interrupted by early electrical impulses that cause the atria to contract too soon, resulting in an extra or premature heartbeat.
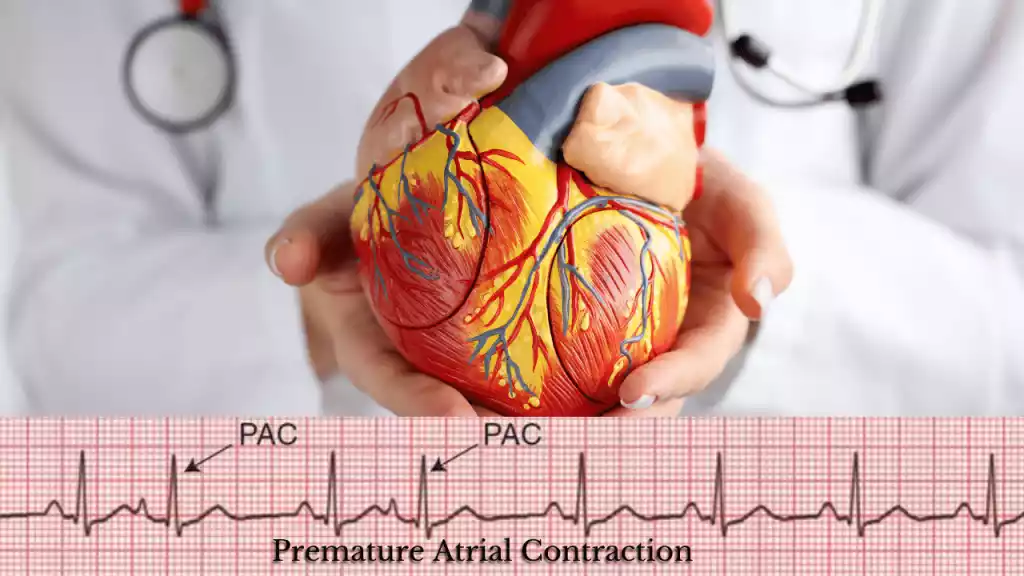
This irregularity can feel like a fluttering sensation or a skipped beat in the chest. PACs are usually harmless and often occur sporadically in healthy individuals. Frequent or persistent PACs might indicate an underlying heart condition that needs medical evaluation. Treatment for PACs depends on their frequency, associated symptoms, and any underlying heart issues, but in many cases, they may not require specific treatment.
Causes of PAC
Here are some common causes of Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs):
- Stimulants like caffeine, nicotine, or certain medications (such as decongestants or asthma drugs)
- Stress or anxiety
- Fatigue or lack of sleep
- Excessive alcohol or drug use
- High blood pressure or heart disease
- Electrolyte imbalances (e.g., low potassium)
- Thyroid disorders
- Stimulants that affect the heart (like some herbal supplements or energy drinks)
- Structural abnormalities in the heart
- Aging or natural wear and tear on the heart’s electrical system
Symptoms of PAC
Here are the symptoms of Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs):
- Fluttering or palpitations in the chest
- Sensation of skipped heartbeats
- Irregular heartbeat
- Brief pause in the heart’s regular rhythm followed by a stronger heartbeat
- Fatigue or tiredness, especially if PACs are frequent or persistent
- Anxiety or uneasiness related to the irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness or lightheadedness in some cases
- Chest discomfort or pain, though this is less common and may suggest a more serious issue if experienced alongside PACs
What is Sinus Arrhythmia?
Sinus arrhythmia is a common and usually harmless irregularity in the heart’s rhythm that occurs during the normal breathing cycle. Unlike other arrhythmias that might signal a heart problem, sinus arrhythmia is typically a variation of the heart rate associated with breathing.

During sinus arrhythmia, the heart rate increases slightly during inhalation and decreases slightly during exhalation. This variability in the heart rate is due to changes in the activity of the vagus nerve, which regulates the heartbeat. It’s more noticeable during slower, relaxed breathing and tends to be more prominent in younger individuals.
Sinus arrhythmia is generally considered a normal finding, especially in children and young adults. It often doesn’t require treatment unless it’s accompanied by other heart-related symptoms or conditions. In many cases, it does not indicate any underlying heart problem and doesn’t cause any adverse health effects.
Causes of Sinus Arrhythmia
Here are the causes or contributing factors to sinus arrhythmia:
- Respiration: The primary cause is the natural interaction between the respiratory system and the heart. The heart rate tends to increase during inhalation and decrease during exhalation due to the influence of the vagus nerve.
- Age: Sinus arrhythmia is more commonly observed in children and young adults. As individuals age, this pattern might diminish.
- Physical Fitness: Athletes or individuals with high cardiovascular fitness levels might exhibit more pronounced sinus arrhythmia.
- Vagal Tone: Variations in the activity of the vagus nerve, which plays a significant role in regulating the heart rate, can contribute to sinus arrhythmia.
- Emotional State: Changes in emotional state or stress levels might affect breathing patterns and, subsequently, influence sinus arrhythmia.
- Medication or Health Conditions: Certain medications or health conditions affecting the heart’s autonomic nervous system could potentially influence sinus arrhythmia, though this is less common.
Symptoms of Sinus Arrhythmia
Here are the symptoms associated with sinus arrhythmia:
- Irregular Heartbeat: The primary symptom is an irregularity in the heart rate, often noted as a change in heart rhythm during breathing cycles.
- Palpitations or Fluttering Sensation: Some individuals might feel a sensation of fluttering or palpitations in their chest due to the variations in heart rate.
- Usually Asymptomatic: In many cases, sinus arrhythmia doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms and might only be detected during a routine medical examination.
- Synced with Breathing: The irregular heart rhythm tends to synchronize with the breathing cycle, increasing during inhalation and decreasing during exhalation.
- Rarely Associated Symptoms: It’s important to note that sinus arrhythmia typically doesn’t cause dizziness, fainting, chest pain, or other significant symptoms commonly seen with more concerning heart conditions.
Comparison table of PAC and Sinus Arrhythmia
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the differences between Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) and Sinus Arrhythmia:
| Aspect | Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) | Sinus Arrhythmia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Early, abnormal contractions in the atria of the heart, causing premature beats | Irregularity in the heart’s rhythm, primarily associated with the breathing cycle |
| Origin | Originates in the atria due to abnormal electrical impulses | Arises from the interaction between the heart and the respiratory system, involving the vagus nerve |
| Cause | Various factors like stress, stimulants, heart disease, electrolyte imbalances | Influenced by respiration, age, physical fitness, and vagal tone |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, fluttering in the chest, irregular heartbeat, possible fatigue | Irregular heartbeat synchronized with breathing, usually asymptomatic or minor palpitations |
| Health Implications | Usually harmless, but frequent occurrences may indicate an underlying heart condition | Generally benign and considered a normal variation in heart rhythm |
| Treatment | Often no specific treatment needed; management targets underlying causes if identified | Typically does not require treatment unless associated with other cardiac issues or symptoms |
| Diagnosis | Diagnosed through electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) and assessment of symptoms | Diagnosed through ECG/EKG and examination during routine check-ups or cardiac evaluations |
| Prognosis | Prognosis depends on the frequency, underlying heart conditions, and associated symptoms | Generally good prognosis; does not typically lead to significant health issues |
This table provides a general comparison, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis, evaluation, and appropriate management of any cardiac irregularities or concerns.
Similarities between PAC and Sinus Arrhythmia
While Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) and Sinus Arrhythmia are distinct cardiac irregularities, they share some similarities:
- Both are Heart Rhythm Irregularities: PAC and Sinus Arrhythmia involve irregularities in the heart’s rhythm, but they arise from different mechanisms.
- Commonly Benign Conditions: In most cases, both PAC and Sinus Arrhythmia are benign conditions and don’t lead to severe health issues.
- Detection via ECG/EKG: Both conditions can be detected through an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), a diagnostic test that measures the heart’s electrical activity.
- May Be Asymptomatic: Often, both conditions may not cause noticeable symptoms or may only produce minor symptoms such as palpitations or irregular heartbeat.
- Typically Don’t Require Treatment: Unless accompanied by other concerning symptoms or underlying heart issues, both PAC and Sinus Arrhythmia usually don’t require specific treatment.
- Can Be Diagnosed During Routine Exams: These irregularities might be incidentally discovered during routine medical examinations or diagnostic tests, even in individuals without significant cardiac symptoms.
Management and Treatment Approaches
The management and treatment approaches for Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) and Sinus Arrhythmia often differ due to their distinct causes and implications.

Management and Treatment of Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC):
- Identification of Underlying Causes: If identifiable triggers (such as caffeine, stress, medications) contribute to PAC, management often involves minimizing or eliminating these triggers.
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle modifications like reducing caffeine intake, managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding stimulants can help reduce PAC occurrences.
- Medical Intervention: In cases where PACs are frequent, bothersome, or associated with underlying heart conditions, medical treatment might involve medications to control symptoms or manage underlying heart issues.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring through electrocardiograms (ECGs) or Holter monitoring (a continuous ECG for a longer duration) might be recommended to assess the frequency and pattern of PACs.
Management and Treatment of Sinus Arrhythmia:
- Reassurance and Observation: As sinus arrhythmia is often considered a normal variation, reassurance and observation without specific treatment are typical, especially when it’s asymptomatic or minor.
- Focus on Underlying Factors: If sinus arrhythmia causes significant symptoms or is associated with other heart conditions, addressing underlying factors such as stress, anxiety, or respiratory issues may be helpful.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular check-ups and cardiac assessments may be advised to monitor any changes or developments in the heart rhythm.
- No Specific Treatment: Generally, sinus arrhythmia does not require specific treatment unless it’s causing concerning symptoms or is associated with underlying cardiac problems.
Common Aspects in Management:
- Healthy Lifestyle: For both conditions, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding excessive stimulants or triggers, is often recommended.
- Regular Follow-ups: Periodic check-ups and follow-ups with a healthcare professional are important for monitoring and managing any changes in heart rhythm.
The treatment and management approach for cardiac irregularities like PAC and Sinus Arrhythmia should be individualized based on the patient’s specific symptoms, overall health, and underlying conditions. Consulting a healthcare provider is crucial for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and tailored management.
Impact on Daily Life and Activities
The impact of Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) and Sinus Arrhythmia on daily life and activities can vary based on their frequency, severity, and associated symptoms:
PAC:
- Mild Impact: For many individuals, infrequent PACs might have minimal impact on daily life, allowing normal activities without significant interruption.
- Emotional Impact: Frequent or bothersome PACs might cause anxiety or stress due to the perception of irregular heartbeats.
- Limitations in Certain Activities: In severe cases or when PACs are associated with other heart conditions, a healthcare provider might advise avoiding certain strenuous activities or stimulants that could exacerbate the irregular heartbeat.
Sinus Arrhythmia:
- Often Asymptomatic: As sinus arrhythmia is usually benign and often asymptomatic, it typically doesn’t hinder daily activities.
- Mild Symptoms: Minor symptoms like palpitations during breathing cycles might be noticed, but they rarely significantly impact daily life.
- No Major Limitations: In most cases, individuals with sinus arrhythmia can carry out regular activities without limitations.
General Impact:
- Emotional Well-being: Both conditions might cause emotional stress or anxiety, particularly if symptoms are noticeable or concerning.
- Adaptation: With appropriate management and understanding of triggers, many individuals can adapt their lifestyles to minimize the impact of these irregularities.
- Quality of Life: If symptoms are severe or persistent, they might affect the overall quality of life, leading to lifestyle modifications or seeking medical advice.
It’s essential to maintain open communication with a healthcare provider to ensure appropriate management, reassurance, and guidance tailored to individual circumstances. Generally, with proper understanding and management, many individuals with these irregularities can lead relatively normal lives without significant restrictions in daily activities.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention Tips
Here are some lifestyle changes and prevention tips that can help manage or reduce the impact of cardiac irregularities like Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) and Sinus Arrhythmia:
Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit the intake of processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sugars.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity as advised by your healthcare provider. Exercise helps promote overall cardiovascular health and can positively impact heart rhythm.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness to lower stress levels, which can contribute to arrhythmias.
- Limit Stimulants: Reduce or avoid stimulants like caffeine, nicotine, and certain medications that can trigger or exacerbate irregular heartbeats.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritize good sleep hygiene by ensuring adequate sleep duration and quality. Lack of sleep can impact heart health and contribute to irregularities.
- Maintain Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated, as dehydration can sometimes trigger arrhythmias.
Prevention Tips
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule routine check-ups with your healthcare provider for cardiac assessments, especially if you have a history of heart issues or risk factors.
- Monitor Heart Health: If you’ve experienced irregular heartbeats or have been diagnosed with arrhythmias, follow your doctor’s advice on monitoring techniques or devices.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol: Limit alcohol intake, as excessive consumption can potentially trigger arrhythmias.
- Understand Medications: Be aware of the potential side effects of medications and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting. Smoking can have detrimental effects on heart health and worsen arrhythmias.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about your condition, its triggers, and management strategies. Understanding your health can help you make informed decisions.
Latest Research and Advancements in Treatment
Research in the field of cardiac arrhythmias, including Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) and Sinus Arrhythmia, focused on several areas:
- Treatment Strategies: Continued research aims to refine treatment strategies for arrhythmias, exploring novel medications or interventions to manage symptoms or reduce the frequency of PACs, especially in cases where they significantly impact quality of life.
- Risk Assessment and Prediction: Advancements in technology and data analysis techniques seek to improve risk assessment and prediction models for arrhythmias, aiding in the identification of individuals at higher risk of developing more severe cardiac issues related to PACs or other irregular heart rhythms.
- Technological Innovations: Ongoing developments in medical devices, such as implantable cardiac monitors or wearable sensors, aim to provide better monitoring capabilities, enabling more accurate detection and analysis of arrhythmias, including subtle variations in heart rhythm like Sinus Arrhythmia.
- Precision Medicine: Research explores the concept of precision medicine to tailor treatment approaches based on individual characteristics, including genetic factors, to optimize outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
- Non-pharmacological Interventions: Studies investigate non-pharmacological interventions, such as lifestyle modifications, behavioral therapies, or targeted therapies, to manage arrhythmias and improve overall cardiac health.
- Electrophysiology Techniques: Advancements in electrophysiology techniques and procedures aim to refine diagnostic and treatment approaches for various arrhythmias, including those originating from the atria.
Given the continuous nature of scientific research, there might have been advancements or new findings in the field beyond my last update. Staying informed through recent medical journals, conferences, or consulting healthcare professionals specializing in cardiology would provide the most current information regarding the latest research and advancements in treating cardiac arrhythmias.
Seeking Professional Help and Consultation
Seeking professional help and consultation for any cardiac irregularities, including Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) or Sinus Arrhythmia, is essential for proper evaluation, guidance, and management.
Here’s what you should consider:
- Primary Care Physician or Cardiologist: Start by scheduling an appointment with your primary care physician who can assess your symptoms and may refer you to a cardiologist for a more specialized evaluation if needed.
- Specialist Consultation: A cardiologist, as a heart specialist, can conduct specific tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), Holter monitor, or echocardiogram, to diagnose and determine the nature and severity of the arrhythmia.
- Share Your Symptoms: Be sure to communicate your symptoms clearly, including any palpitations, irregular heartbeats, or related discomfort you’re experiencing. Describe the frequency, duration, and any triggers you’ve noticed.
- Medical History and Lifestyle Habits: Provide details about your medical history, any existing conditions, medications you’re taking, and lifestyle habits (e.g., caffeine intake, stress levels, exercise routine) that might contribute to or affect the arrhythmia.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions or seek clarification regarding your condition, potential causes, available treatments, and management options. Understanding your condition is crucial for your involvement in the treatment plan.
- Follow Recommendations: Follow the advice, treatment plan, and lifestyle recommendations provided by the healthcare professional. This might include medication, lifestyle modifications, or further monitoring.
- Regular Follow-ups: Schedule regular follow-up appointments as advised by your healthcare provider to monitor your condition, assess treatment effectiveness, and make any necessary adjustments to your management plan.
Timely consultation and collaboration with healthcare professionals specialized in cardiology are crucial for accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and ensuring the best possible outcomes for individuals experiencing cardiac irregularities.
Final Opinion
Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) involve early atrial heartbeats, often harmless but possibly indicating underlying conditions. Sinus Arrhythmia presents as a normal heart rate variation linked to breathing cycles. While typically benign, both require evaluation if symptomatic. Lifestyle changes, stress management, and medical guidance aid in managing these irregularities for improved cardiac health and quality of life.