Benzene and Phenyl
Benzene and Phenyl are two important organic compounds, with distinctive characteristics and uses.
Benzene has the molecular formula C6H6 is a non-colorless liquid with an unique structure that is comprised of a six-membered carbon ring, which has double bonds. The structure of benzene gives it its aroma and stability because of the delocalization of electrons in the form of p-electrons. It is extensively used in industries like Petrochemicals and serves as precursors for the creation of detergents, plastics and pharmaceuticals. But benzene is recognized as a carcinogen and requires care when handling it and strict precautions for safety.
Phenyl On contrary, is referring to a substitution that comes from benzene, by taking away the hydrogen-atom. The symbol is -C6H5 and can be present as a component of different chemical compounds. Phenyl groups retain the stability and aromaticity of benzene, but does not have the entire six-membered ring structure. Phenyl groups play a crucial role in organic chemistry. They are particularly important for pharmaceuticals. They confer specific properties on molecules like enhanced the binding affinity of molecules or lipophilicity. These are also utilized in the field of materials sciences, dyes, as well as flavors.
The distinction between benzene and Phenyl is essential for researchers as well as chemists and experts across a variety of fields. In contrast to benzene, which is the main compound that has its own unique characteristics and structure while phenyl represents the substituted benzene which plays an important function in molecular characteristics and applications. Knowing their chemical structure and physical properties, as well as their nomenclature, reactivity and industrial applications ensures the that they are safe and efficient in the use of these chemicals in different applications in both industrial and academic.
What are important points about benzene and phenyl ?
- It is a cyclic, cyclic hydrocarbon with a molecular formula C6H6, whereas phenyl is a reference to a substitute that is derived from benzene through the removal of the hydrogen atom.
- Benzene is unique in its structure made up of a 6-membered carbon ring, which has double bonds. This gives its aroma and stability due to delocalization of P-electrons.
- Phenyl retains the aroma and stability that benzene has however does not have the full six-membered ring structure. It is typically referred to by the symbol -C6H5 in a variety of substances.
- The liquid Benzene has a strong odor and is volatile with a distinct sweet scent. It is extensively used in industries like petroleum chemicals, and is used as precursor to the creation of detergents, plastics and pharmaceuticals. However, benzene can be known to cause cancer and needs extreme safety measures.
- Phenyl group plays a significant part in organic chemical. They are found in a variety of compounds, but are particularly prevalent in pharmaceuticals. They confer specific characteristics to molecules, for instance an increased affinity for binding or lipophilicity.
- The main function of benzene is in reactions of substitution in which one or more hydrogen atoms in the benzene rings are substituted by functional groups. It’s fairly solid and stable, but it is more reactive to the addition reaction.
- Phenyl, as a substitution is able to undergo the same substitution reactions like benzene. It is dependent on the properties of the molecules to which it is connected. Phenyl’s reactivity is dependent upon the functional groups linked to their.
- Both benzene and Phenyl are used in important applications across a variety of industries like pharmaceuticals materials science, dyes flavors, as well as petrochemicals.
- Knowing the difference between benzene and Phenyl is essential for scientists as well as chemists and experts working in fields like organic chemical chemistry, industrial production and research in pharmaceuticals, for ensuring safe and efficient usage of these chemicals.
Definition of Benzene
It is an organic chemical compound that has an molecular formula, C6H6. It’s a transparent liquid at room temperature and recognized by its distinct scent that is sweet. The term Benzene refers to an hydrocarbon and specifically as an aromatic chemical due its distinct and robust form and.
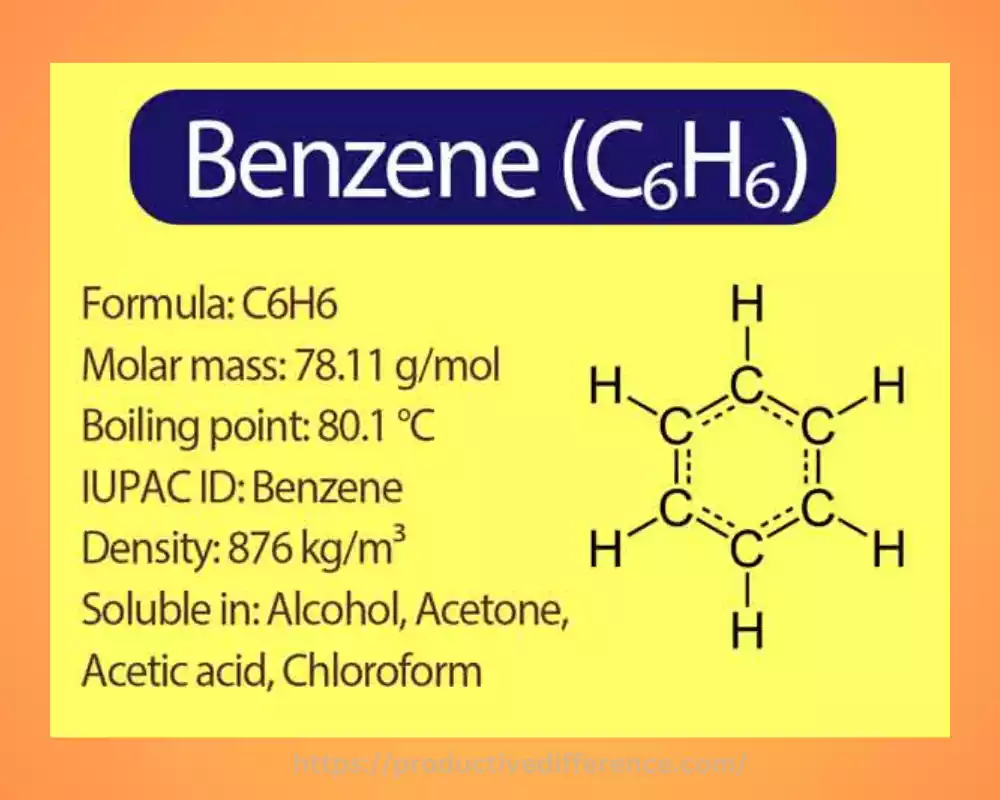
The benzene structure consists of a six-membered carbon circle and every carbon atom being bonded to a hydrogen atom. Carbon atoms within the benzene rings are joined through alternating double and single bonds. The result is an equilibrating hybrid structure. Delocalization of the p-electrons results in an electron-rich cloud with a circular density, both above and beneath the plane of carbon atoms which gives benzene its aromatic properties.
The compound Benzene plays a significant role for a wide range of industries. It plays an essential part in the production of various chemical compounds and synthetic fibers, used as solvents or components in making plastics, detergents and pharmaceutical products, synthetic fibers or many other things. But be warned: it can be very toxic with serious health repercussions if taken in large doses.This includes the possibility of contracting cancer.
Because of its aroma and its stability, benzene displays distinctive chemical properties. It is primarily performing substitution reactions as opposed to adding reactions. The substitution reactions are the substitution of hydrogen atoms in the benzene ring by other functional groups leading to the creation of a variety of derivatives.
Definition of Phenyl
Phenyl stands for a distinct functional group, or substituent, that has been made from benzene, by taking an atom of hydrogen (-H) out of the aromatic ring of benzene. The symbol is”-C6H5″ in which carbonatom (C) is directly attached to the aromatic the ring.

Phenyl groups can be found in organic compounds. They are essential in the determination of chemical and physical properties of molecules they’re attached to. Phenyl groups preserve the aroma and stability of benzene, but does not have the entire six-membered ring structure.
Structure-wise The phenyl group is composed of a benzene ring, devoid of any substitutes. The most common way to visualize it is as a sphere that is joined with the remainder of the molecule with only one bond.
Phenyl groups are found throughout a variety of substances in a variety of disciplines, like pharmaceuticals material science, dyes flavors, and many numerous other. Phenyl groups can confer specific characteristics to molecules they’re associated with, for example improved lipophilicity, greater binding affinity or chemical reaction.
If they are attached to different molecules, phenyl group may participate in different chemical reactions, such as the substitution reaction that is similar to that of the benzene. Reactivity and behaviour of phenyl group depend on the particular functional groups linked to them as well as the chemical conditions.
In short, phenyl is to a substitute that is made from benzene, and is an isolated structural unit having characteristics that are aromatic. It’s commonly present in organic compounds, and is a key element in the determination of properties and the reactivity of molecules that they are associated with.
Comparison Between Benzene and Phenyl
Phenyl and benzene both possess unique chemical structures which set them apart:
Benzene: Benzene (C6H6) is a hydrocarbon with six carbon atoms connected by hydrogen bonds that forms an hexagonal-shaped ring structure. Each carbon atom links directly with another hydrogen atom.
One of the most distinctive features of benzene lies in its alternate bonding of double and single bonds between the carbon atoms of the circle. It is typically illustrated as a hexagon that has an inner circle to symbolize the p-electrons that are delocalized. Delocalization of electrons results in the resonance hybrid that gives the benzene an aroma and stability. Carbon-carbon bonds found in the compound benzene are of a length that’s between the single bond as well as double bonds.
Phenyl: (-C6H5) is the functional group which is created from benzene through the removal of just one hydrogen atom. The symbol is an phenyl-ring that is in essence a benzene-based the ring, but without additional substituents. The phenyl ring is made up of 6 carbon atoms that form the hexagonal structure of a ring, which has every carbon atom being bonded to a hydrogen atom. The carbon atom of the phenyl ring is directly linked to the molecule that it’s a part of via only one bond. The phenyl ring retains the stability and aromaticity of benzene however it lacks the entire six-membered structure of a ring.
As a summary, benzene can be described as one of the compounds with a 6-membered ring structure. Phenyl can be described as an functional group that is derived from the benzene compound that has been modified structure and an immediate attachment to various molecules.
Physical Properties
The physical properties of benzene as well as Phenyl are different because of their different characteristics.
We will look at their physical characteristics:
Benzene:
- Status and Appearance Benzene is a transparent liquid at room temperature.
- Odor Benzene comes with a distinct sweet scent.
- Volatility Benzene is very volatile. This means that it is able to evaporate quickly.
- Melting Point The melting point for the chemical benzene is 5.5degC.
- Boiling Point Boiling Point: The boiling point for the benzene compound is 80.1degC.
Phenyl:
- The appearance and state of the compound: Phenyl is not a separate compound, but an ingredient that is attached to different molecules. Therefore, it doesn’t have a distinct state or form.
- Impact on Physical Properties the presence of a phenyl-based group within a compound can affect the physical properties of the molecule, including melting temperature, boiling points and
- solubility.
- These properties, however, depend on the general structure and chemical structure of the molecules to which the phenyl group has been connected.
- It’s crucial to understand that phenyl cannot be discovered or viewed in its purest form however, rather it’s a component of different substances. Thus the discussion of the physical properties of phenyl in isolation is not always a good way to gain insight.
- Physical properties for molecules with a phenyl molecule will be influenced by the functional groups, as well as the structures of the molecule in general.
- Chemical Properties and Reactivity
- The physical properties of benzene as well as Phenyl are different because of their different characteristics. We will look at their physical characteristics:
Where is benzene and phenyl used?.
- Benzene:
- Petrochemical Industry Benzene is an essential base material used in the industry of petrochemicals.It’s used to source of energy for the production of a wide assortment of chemical compounds, such as synthetic fibers and plastics solvents and detergents and resins rubber.
- Pharmaceutics Benzene is a component in the production of pharmaceutical substances. It’s used for the manufacture of pharmaceuticals to treat various ailments.
- Solvent Benzene is a solvent that works that is utilized in laboratories and industrial processes to dissolve or extract substances. Due to the toxicity of benzene, its usage as a solvent is decreased or substituted with more safe alternatives.
- Fuel Additive Benzene is a constituent of gasoline that is utilized to enhance the octane level and as an antiknock agent that improves the efficiency of gasoline.
- Reagent for Laboratory Use: Benzene can be used as a reagent for organic synthesis laboratories.
- Industrial Cleaning: Solvents based on benzene can be used for cleaning to degrease, remove adhesives as well as general industrial cleaning needs.
- Phenyl:
- Phenyl groups in pharmaceuticals typically are found in the pharmaceutical industry. They may improve the lipophilicity and efficacy of pharmaceuticals, increase their permeability or alter the binding affinity of drugs, leading to the desired pharmacological effect.
- Material Science: Phenyl-containing substances can be used in material science to create the polymers, coatings, special materials, as well as adhesives.
- Colorants and Dyes: Phenyl compounds play a role in the development of dyes and pigments that can be used in a variety of sectors, such as textiles, printing as well as cosmetics.
- Flavorings and Fragrances: Phenyl-groups are responsible for the aromatic characteristics of flavors and scents within the food, beverage and perfumery sectors.
- Organic Synthesis: Phenyl group are typically used as multi-functional components in organic synthesis. They are used to create certain chemical properties or to alter the characteristics of molecules.
- It is important to remember that the use of benzene as well as phenyl could be different based upon regional laws as well as industry-specific regulations. Additionally, the usage of benzene is becoming more controlled because of its toxic character as well as safer alternatives seeking out whenever it is it is.
Comparison Table
comparison between benzene and phenyl in a tabular format:
| Aspect | Benzene | Phenyl |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds | Derived from benzene, represents a phenyl group |
| Usage | Petrochemical industry, solvents, pharmaceuticals, fuel additive, laboratory reagent | Pharmaceuticals, materials science, dyes, flavorings, organic synthesis |
| Reactivity | Primarily undergoes substitution reactions, relatively stable and less reactive towards addition reactions | Can undergo similar substitution reactions, reactivity depends on attached functional groups |
| Physical Properties | Colorless liquid, sweet odor, highly volatile, melting point of 5.5°C, boiling point of 80.1°C | No standalone physical properties, properties dependent on the molecule it is part of |
| Representation | Hexagonal ring with alternating single and double bonds | Circle connected to the rest of the molecule |
| Health Considerations | Known carcinogen, requires strict safety measures | Safety considerations depend on the molecule it is part of |
summary
A cyclic hydrocarbon that has a distinctive structure made up of a six-membered carbon circle which has double and single bonds. It is very stable, and displays aromaticity because of the delocalization of electrons in the form of p-electrons. It is widely used in a wide range of industries, which include the pharmaceuticals industry, plastics and petrochemicals. In addition, it is utilized to create solvent and also an additive. But, benzene is an established carcinogen that requires extreme safety precautions for its use and handling.