Introduction
Macrocephaly refers specifically to a situation in which an individual’s head circumference exceeds the typical dimension for age as well as gender. The reason for this may be due to many factors, such as benign family traits or diseases like hydrocephalus. These are that is defined by the increase in cerebrospinal fluid inside the brain. Hydrocephalus is characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain’s cavity, leading to an increase in pressure on the brain.
Although macrocephaly is identified by a larger head hydrocephalus may be the result of this increase and cause a variety of symptoms like nausea, headaches vision issues, and the development of slowdowns. Treatment options for both conditions usually consist of monitoring and managing the issues, and for the case of hydrocephalus, surgical procedures like shunt placement or endoscopic procedures that relieve pressure inside the brain. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential in dealing with these issues and minimizing the risk of complications.
Definition of Macrocephaly
Macrocephaly is a condition that is defined by an abnormal expansion or an increase on the face, particularly in reference to an abnormally larger head circumference, which is greater than the normal range for individuals of a certain age and gender. The condition is usually noticed in young children and infants when the head appears larger compared to the body or typical growth charts for children.
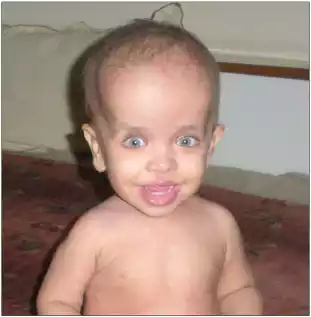
Although some instances of macrocephaly are benign and not a sign of any underlying health issue, it could be indicative of disorders or conditions that are underlying such as genetic causes as metabolic disorders or diseases like hydrocephalus which is a condition where the increase in cerebrospinal fluid inside the brain may result in the head growing.
Treatment and management for macrocephaly depends on determining the reason, observing the growth of the head and symptoms that accompany it, and, if required taking care of any medical conditions that cause the head’s abnormal size.
Definition of Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a neurologic condition that is characterized by an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain spaces (ventricles) in the brain. This over-accumulation of fluid causes an increase in pressure within the skull, which could cause injuries to brain tissues.
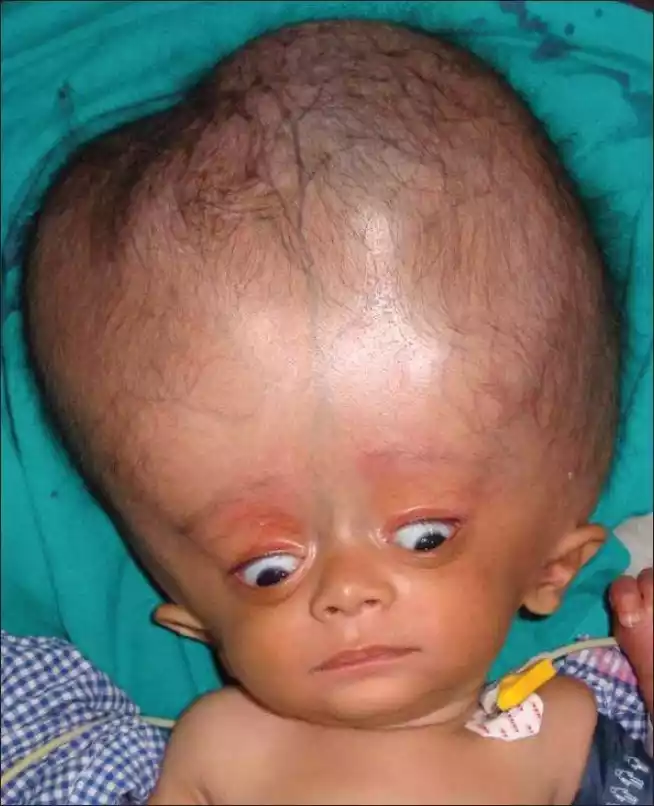
Hydrocephalus can happen at any age and can be caused by a variety of factors like an obstruction that hinders the absorption or flow of CSF or excessive production of CSF and bleeding in the brain or brain, cancer, infections or developmental problems that are congenital. The condition may cause various symptoms, including an increased head (in infants) nausea, headaches as well as vision problems cognitive impairment, trouble walking and incontinence.
Treatment usually involves surgical interventions for example, the installation of a shunt system that will transfer fluids to a different area of the body to allow to absorb it or, in certain cases alternative methods to make new routes to facilitate CSF drainage. Monitoring and control of CSF flow is essential to avoid complications that are associated with the increased pressure inside the skull.
What is the causes of Macrocephaly?
Macrocephaly is an abnormal growth on the forehead, may be caused by a variety of factors. The main causes that cause macrocephaly are:
- Familial macrocephaly that is benign: In certain instances an increased head size could be inherited by families without causing any health problems.
- Hydrocephalus: It is a condition is characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, could result in macrocephaly since the increase in volume of fluid causes the head to expand.
- Genetic Syndromes: Certain genetic conditions or syndromes like Sotos syndrome or Weaver syndrome or any other disorders of genetic origin, could be associated with macrocephaly as one their characteristics.
- Metabolic Disorders: Particular metabolic issues or imbalances can result in an increased head size in conjunction with their clinical manifestation.
- Other medical conditions: Some neurological conditions such as brain tumors, neurological disorders, and developmental disorders could be a contributing factor to macrocephaly because of their effects on the growth of the brain and its development.
What is the causes of Hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus can result from a variety of causes. All of them affect the flow of blood or absorption of cerebrospinal liquid (CSF) in the brain. The main causes are:
- Obstruction to CSF flow: The obstructions in these pathways that permit CSF to circulate normally can result in hydrocephalus. These blockages may be caused by conditions like birth defects such as cysts, tumors or lesions within the brain which block the circulation of CSF.
- Insuficiency of CSF: In some instances, the brain may produce an excessive amount CSF that could lead to hydrocephalus. This scenario is extremely rare in comparison to those that are caused by blocked flow or a lack of absorption.
- The Complications of Birth: The brain is prone to bleeding (intraventricular hemorrhage) and diseases (such like meningitis) or some growth abnormalities in fetal development could cause hydrocephalus to infants.
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI): Head trauma, and particularly severe brain injuries, can alter the normal flow or absorption of CSF and cause hydrocephalus.
- Brain Cysts or Tumors: Cysts or tumors within the brain may interfere with CSF absorption and circulation and can contribute to the development of hydrocephalus.
- Unknown or Idiopathic causes: In some instances the cause of hydrocephalus may not be determined, a condition known as Idiopathic Hydrocephalus.
Symptoms of Macrocephaly
Here are a few common signs of macrocephaly:
- Larger Head Size: The primary symptom is when the head circumference is significantly larger than the average for an individual’s age and gender.
- Rapid Head Growth: A rapid increase in the size of the head over a brief time period, usually beyond the normal growth rate.
- Disproportionate Appearance: The head can appear larger than the body or its peers.
- The bulging Fontanelle (Soft Spot): In infants the soft spot on the baby’s forehead can bulge due to the more pressure in the skull.
- development delays: There are instances macrocephaly may be connected with neurodevelopmental delays or problems.
- Signs of increased intracranial pressure: These can be symptoms such as headaches vomiting, and irritability. In more serious instances, vision problems or balance.
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus
Here are the most common symptoms that are common to hydrocephalus:
- Expanded Head (in infants): A rapid increase in the head circumference or an unusually big head compared to the body or aged peers.
- A bulging Fontanelle (Soft Spot): Increased pressure within the skull could result in the soft area on the infant’s head to expand.
- Headaches: Most often, they are severe and persisting, particularly in adults and older children.
- Vomiting and Nausea: Due to increased intracranial pressure, which affects the brain’s functions.
- Vision Issues: Blurred vision, difficult focusing, or any different visual problems.
- Cognitive Impairment: Memory problems, difficulties in concentrating or concentrating, and changes in personality or behavior.
- Gait disturbances: Difficulty walking, or keeping equilibrium.
- Urinary Incontinence: Loss of bladder control.
- Lethargy or sleepiness: Feeling excessively tired or sleepy.
Treatment Options for Macrocephaly and Hydrocephalus
The management and treatment strategies for hydrocephalus and macrocephaly differ due to their different reasons and the fundamental mechanisms.
Here’s a brief overview of the strategies for each of the conditions:
Management of Macrocephaly:
- Watching and Monitoring: Monitoring regularly of head development and growth milestones is essential, particularly for infants and children.
- Treatment of Underlying Conditions: If macrocephaly is caused by an underlying source, such as hydrocephalus or genetic disorders treatment of the underlying condition is crucial.
- The treatment for symptomatic disorders: Managing associated symptoms and developmental delays, when they are present. It may involve therapies like occupational therapy, physical therapy or speech therapy depending on the individual’s needs.
- Surgery: In cases where macrocephaly results from issues like hydrocephalus or other conditions surgery may be required to ease the pressure upon the brain. This could include interventions to treat the root reason, such as placement of shunts or the endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) for hydrocephalus.
Approaches to Treating Hydrocephalus:
- Surgical Interventions:
- Shunt placement: Most common treatment involves the surgical placement of the shunt, or an elongated tube that is used to divert the excess CSF out of the brain other parts of the body, where it will be taken in (e.g. the abdomen or the heart).
- Endoscopic 3 Ventriculostomy (ETV): In certain instances an operation that creates an entirely new route to CSF circulation within the brain could be done instead of shunt positioning.
- Continuous Monitoring: After surgery, patients require regular check-ups to make sure that the ETV shunt is functioning properly in addition to making any required adjustments.
- Adjustments and Management of Complications: Shunts could require adjustments or revisions as time passes due to complications like infection, blockage or a malfunction. The prompt recognition and management of these issues is essential.
- Alternate Treatments: Certain situations advanced approaches like minimally invasive methods or imaging technology that are advanced could be a possibility for treating hydrocephalus.
- Multidisciplinary care: Long-term care often involves a multidisciplinary team which includes neurosurgeons, neurologists therapists, pediatricians and other specialists, in order to meet the ever-changing needs of patients who suffer from hydrocephalus.
Treatment for hydrocephalus is intended to relieve symptoms, lower intracranial pressure, and to prevent complications. The decision to treat is based on a variety of aspects, such as the root causes, age, overall health and personal circumstances for the individual patient.
Comparison Table of Macrocephaly and Hydrocephalus
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Macrocephaly and Hydrocephalus:
| Aspect | Macrocephaly | Hydrocephalus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abnormal enlargement of the head beyond expected size | Accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) causing pressure |
| Primary Feature | Enlarged head size disproportionate to body or peers | Abnormal buildup of CSF in the brain causing increased pressure |
| Causes | – Benign familial traits
– Underlying conditions like hydrocephalus, genetic syndromes, metabolic disorders |
– Obstruction/blockage of CSF flow
– Overproduction of CSF – Tumors, infections, birth complications |
| Symptoms | – Enlarged head size
– Rapid head growth – Developmental delays (if related to underlying conditions) |
– Enlarged head (in infants)
– Headaches, nausea, vomiting – Vision problems, cognitive issues – Gait disturbances, urinary incontinence |
| Associated Conditions | Can be associated with underlying neurological disorders | Can lead to developmental issues, damage to brain tissues, neurological complications |
| Treatment | – Monitoring head growth
– Addressing associated symptoms – Treating underlying conditions (if present) |
– Surgical interventions (shunt placement, ETV)
– Management to alleviate CSF buildup and pressure |
| Relation | Can be a symptom related to various conditions including hydrocephalus | Often one of the causes for macrocephaly, but not the only cause |
This comparison table outlines the key differences in terms of definition, primary features, causes, symptoms, associated conditions, treatments, and their relation between Macrocephaly and Hydrocephalus.
Relationship Between Macrocephaly and Hydrocephalus
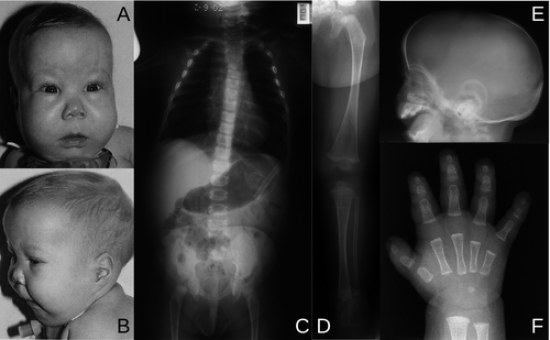
Here are the most important aspects of the relationship with Macrocephaly as well as Hydrocephalus:
- Shared Symptoms: Hydrocephalus can lead to macrocephaly as a result of excessive accumulations of cerebrospinal liquid (CSF) in the brain, leading to an increase in the size of the head.
- Not all the time directly connected: Although Hydrocephalus can cause Macrocephaly, not every case of Macrocephaly can be attributed to Hydrocephalus. Macrocephaly could be a result of other factors, such as metabolic disorders, genetic syndromes or benign genetic characteristics.
- Different conditions: Macrocephaly focuses on the size of the head that is increased while Hydrocephalus specifically identifies the build-up of CSF that causes increased pressure within the skull and its symptoms.
- Treatment variations: While surgical interventions may be required for both types of conditions, the procedure and treatment strategies differ greatly. Hydrocephalus typically requires an endoscopy or shunt placement and treatment for Macrocephaly is based on addressing the root cause in the event of.
- Coexistence is possible: Both conditions can coexist in certain instances, an increased head does not necessarily mean that you have Hydrocephalus. A thorough examination is required to identify the precise root of Macrocephaly.
Even though Hydrocephalus may lead to Macrocephaly due to an excessive CSF concentration, this connection isn’t always straight because Macrocephaly can be caused by a myriad of other reasons that are not related to Hydrocephalus. Understanding the differences is vital to ensure a correct diagnosis and proper treatment for each of the conditions.
Living with Macrocephaly and Hydrocephalus
The experience of living with macrocephaly and hydrocephalus is a unique challenge, for both those affected by these conditions as well as their caregivers.
Here’s a quick overview of the it’s like to live with these conditions:
Living with Macrocephaly:
- Health Monitoring: People with macrocephaly may need regular medical examinations to check the growth of their heads as well as developmental stages.
- Impact on everyday life: Depending on the causes and conditions that are associated people may face difficulties due to the development of neurological disorders, delays in development or other symptoms that are related to the root causes.
- Treatments and interventions: People who are affected may get help from therapies such as occupational therapy, physical therapy or speech therapy, to deal with development delays or other symptoms.
- Social and emotional support: Coping with the disease may require emotional support for the individual affected as well as their families members.
Living with Hydrocephalus:
- Treatment and medical care: Hydrocephalus sufferers typically require ongoing treatment. This means regular medical visits scanning scans for imaging, as well as modifications or revisions to the shunts when needed.
- Potential Complications: There could be the risk of complications that are associated with shunts such as blockages, infections or malfunctions, all of which will require medical attention immediately.
- Impact on daily activities: Depending on the degree of the issue and the related issues, people may be impacted in their everyday activities such as education, work or social activities.
- Support Networks: Communities and support groups are available for people with hydrocephalus as well as their families, offering helpful resources, information as well as emotional help.
Coping Strategies:
- Education and awareness: Knowing the condition and the implications could aid families and individuals to navigate the challenges and make educated choices.
- Access to healthcare: Being able to access specialists and medical treatment is vital to managing these ailments efficiently.
- Flexible Strategies: The implementation of adaptive methods as well as assistive devices or adaptations to address the limitations or difficulties can dramatically enhance your quality of life.
- Advocacy and Support: Advocate for yourself or those you love and seeking out appropriate support services and establishing connections with support networks can be helpful in managing these ailments.
When living with macrocephaly and hydrocephalus may be challenging advances in medical treatment and support networks as well as interventions have dramatically increased the level of quality of life of the many people affected by these disorders. It is essential to have a robust support system, accessibility to medical care and an approach that is proactive to tackling the difficulties related to these conditions.
Research and Advancements in Treatment
Advancements and research for treating macrocephaly as well as hydrocephalus are ongoing with the aim of improving diagnostic precision, increase the treatment options and limit the risk of complications.
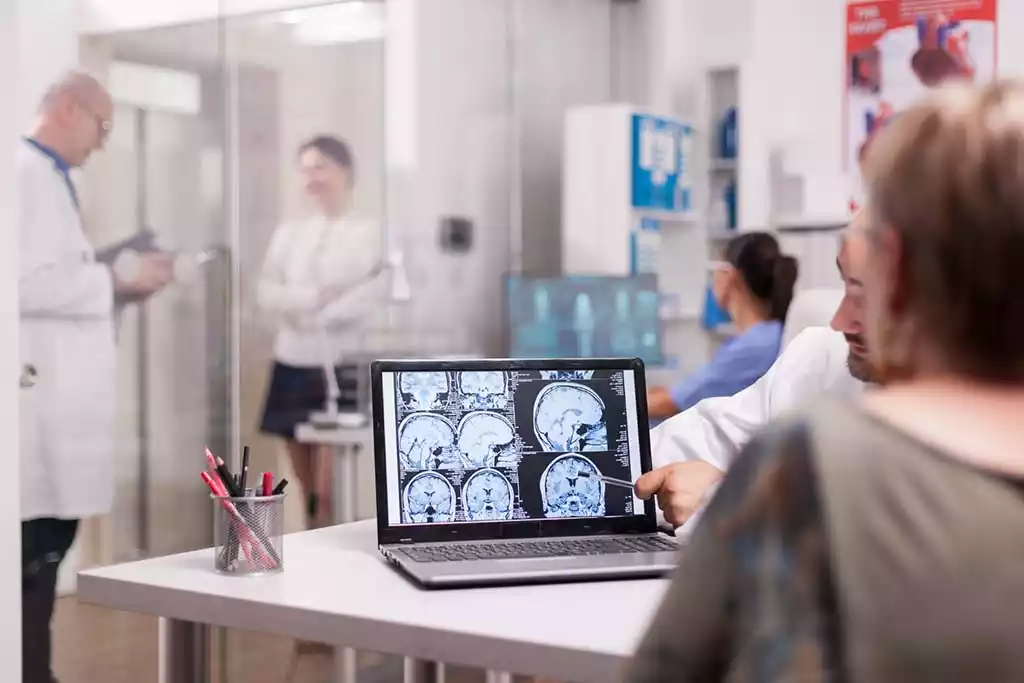
Here are a few notable areas of progress:
Hydrocephalus:
- Shunt Technology: Research is ongoing on the development of Shunt systems that minimize the possibility of complications like blockages or infections, as well excessive drainage, thus enhancing their lifespan and effectiveness.
- Endoscopic procedures: Advancements in endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) methods are designed to improve the efficiency of this procedure offering a viable alternative to shunt placement in certain cases, and improving the outcomes.
- Minimally Invasive Treatments: Researchers are looking into more minimally invasive procedures and new techniques to treat hydrocephalus, possibly reducing the requirement for traditional surgery to shunt.
- Understanding the Causes Behind: Further research into the root causes of hydrocephalus, which includes genetic factors developmental abnormalities, as well as excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid could lead to more specific treatment options.
- Biocompatibility Materials: Innovations made in creation of biocompatible materials that are employed in shunts are designed to lessen the risks of infections and irritation to the tissue.
Macrocephaly:
- Genetic studies: Research focuses on the identification of particular gene-related markers, or mutations linked with macrocephaly. This may lead to targeted treatments or treatments.
- Advanced Imaging Methods: The advancements in image techniques, like MRI help in the early detection, precise diagnosis, and monitoring head growth in patients suffering from macrocephaly.
- Treatment tailored to the underlying conditions: As macrocephaly can be the result of various reasons, targeted treatments specific to these causes, like treating metabolic diseases or genetic disorders, are being researched.
- Early Intervention Strategies: Finding early signs of macrocephaly and implementing strategies to address the development delay or symptoms is a matter of research that could help improve outcomes.
- Precision Medicine Approaches: Precision or personalized medicine strategies could offer better treatments by taking into consideration an individual’s unique metabolic or genetic profile that contributes to macrocephaly.
Shared Areas:
- Multidisciplinary care: Collaborative efforts involving neurosurgeons, neurologists and geneticists, and researchers seek to provide a comprehensive treatment and conduct research for better management of both disorders.
- Clinical trials: Clinical trials are ongoing and examine new surgical methods, and treatments for improved outcomes. minimize the risk of complications, and improve understanding.
- Patient-Centered Care: There’s a growing focus on patient-centered care taking into account the individual’s needs, their the quality of life and long-term outcomes in the design treatments strategies.
Research on macrocephaly and hydrocephalus seeks to improve the existing treatment options, create new strategies, and expand the understanding of the root reasons to provide better and more personalized care for those affected.
Conclusion
Hydrocephalus and Macrocephaly are distinct neurological disorders, but with a few interconnections. Macrocephaly is a condition that causes an abnormal growth of the head. This is usually seen due to an increase in head circumference that is beyond the normal limit for sex and age. It may be caused by a variety of causes, including genetics or metabolic conditions or diseases like hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus is characterized by an abnormal growth of cerebrospinal fluid inside the brain, resulting in an increase in pressure inside the skull. Although it is possible for hydrocephalus to cause macrocephaly, not all instances of macrocephaly can be attributed to hydrocephalus.
Both conditions require specific treatment strategies, which could include surgical interventions or monitoring, as well as addressing the underlying cause or symptoms. Continuous research and advances aim to improve the accuracy of diagnosis treatments, as well as general quality of life for people affected by these conditions.