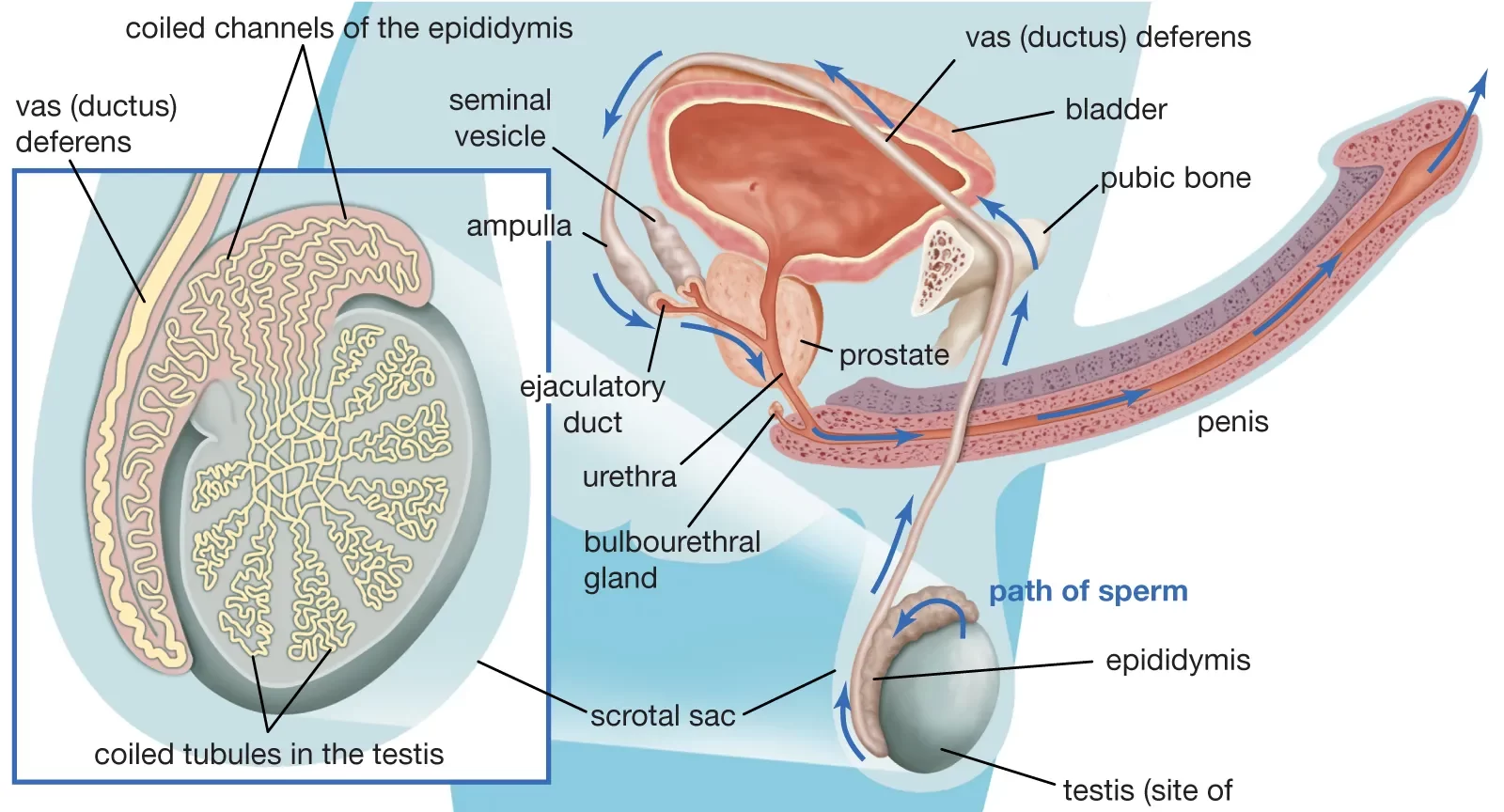
Introduction
The male reproductive system consists of the penis, which comprises three cylindrical masses of erectile tissue: two corpus cavernosum and one corpus spongiosum. The corpus cavernosum, situated on the dorsal side of the penis, is responsible for the bulk of penile rigidity during an erection. It contains numerous blood-filled spaces called lacunae, which engorge with blood upon arousal, causing the penis to stiffen and enlarge.
The corpus spongiosum, positioned on the ventral side, encases the urethra and remains relatively spongy during an erection, ensuring the urethra remains open for the passage of semen and urine. Both the corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum play pivotal roles in the physiological process of achieving and maintaining penile erection, which is crucial for sexual function and reproduction.
Definition of Corpus Cavernosum
The corpus cavernosum is one of the two conical erectile tissues located in the penis (in males) and the clitoris (in females). In males, there exist two corpus cavernosum erectile structures on the dorsal aspect of the penis. When sexual stimulation occurs the cavernous areas expand with blood, which causes the penis to become stiff and erect. The corpus cavernosum comprises a blood-filled network called lacunae.
These spaces expand and engorge themselves with blood after stimulation, aiding in achieving and sustaining an erection by trapping blood inside the tissue. The erectile tissue is essential to sexual function in males and helps to maintain the penile stiffness required to allow sexual intimacy and reproduction.
Definition of Corpus Spongiosum
The corpus is a specially designed erectile tissue shaped like a cylinder inside the male reproductive system. It lies on the penis’s ventral (underside) part of the penis. In contrast to the corpus cavernosum paired it is the only corpus spongiosum within the penis. Its main function is to protect the urethra, a tube through which semen and urine travel.
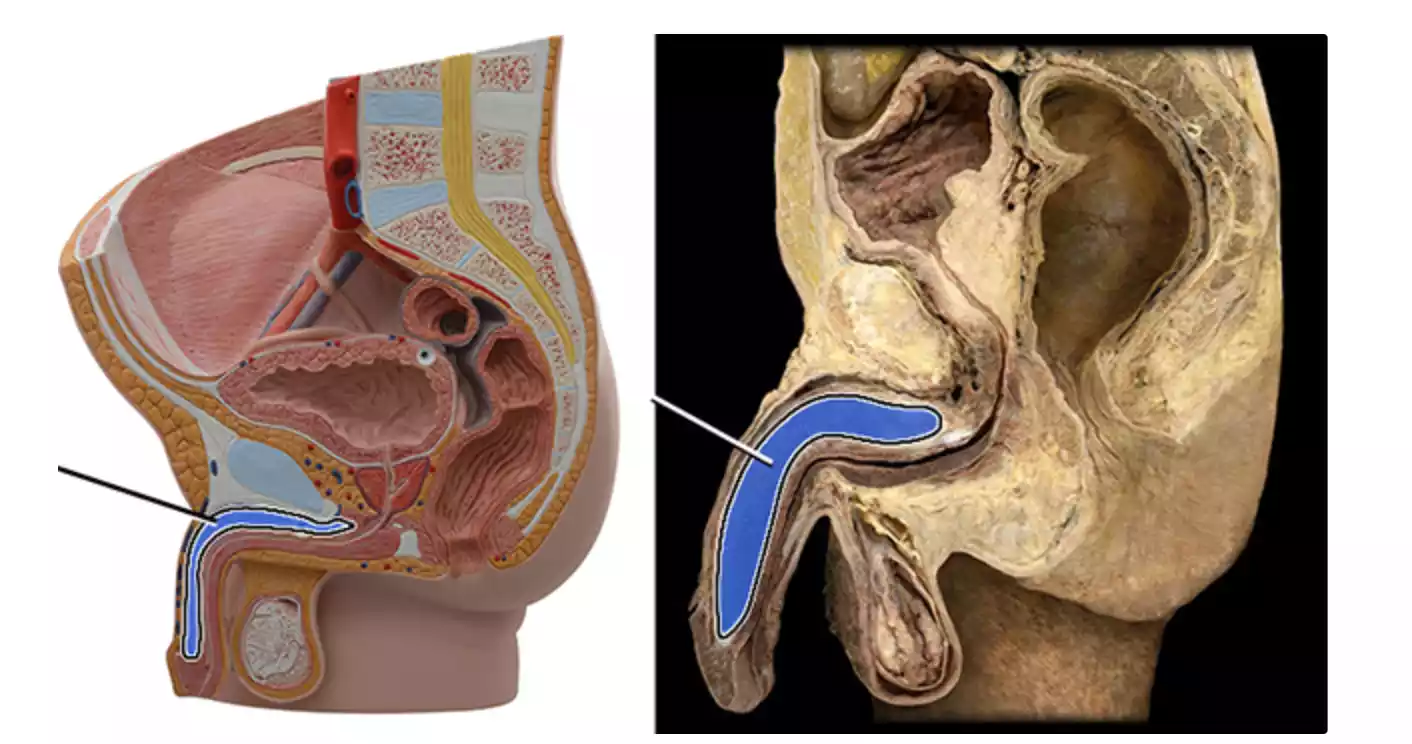
When sexual stimulation occurs when sexual stimulation occurs, the corpus is filled with blood, which contributes to the stiffness of the penis. But unlike the cavernosum the corpus spongiosum is spongy enough to ensure that the urethra is open, allowing the flow of both semen and urine. This structure plays an important function in maintaining the functioning of the urethra in the erection process, which allows for ejaculation as well as the flow of fluids.
Importance of knowing the difference between Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum
The distinction between corpus cavernosum and the corpus spongiosum is vital because of their important role on male reproductive health as well as sexual function
- Function of erection: The corpus cavernosum is the primary reason for the majority of penile rigidity in an erection. It is filled with blood and can are engorged with blood, which causes the penis to stiffen and to expand. The corpus of spongiosum, is a bit spongy in an erection. This helps ensure the urethra’s integrity for the flow of fluids.
- Protection of the urethra: The corpus spongiosum protects the urethra by encasing it, offering security and ensuring its openness during the erection process. This stops the constriction of the urethra and permitting the flow of both semen and urine without obstruction.
- Sexual purpose: Both structures are essential for sexual function and reproduction. The capacity of the corpus cavernosum’s corpus to engorge itself with blood is crucial to achieving the maintenance of an erection, which facilitates sexual intimacy. The corpus spongiosum makes sure that the urethra stays active and functioning, which allows for ejaculation and passage of reproductive fluids.
- Clinical importance: Understanding the anatomy and function of these structures is essential for diagnosing and treating problems that affect male sexual health for example, erectile disorders (issues with the ability of the corpus cavernosum to fill up with the blood) or urethral disorders (issues related to the corpus spongiosum, and its enclosure of the urinary tract).
Understanding the distinctions between the corpus cavernosum and the corpus spongiosum is crucial to understand their roles in regulating penile function and maintaining urethral patency and addressing any health issues in male reproductive health and sexual health.
Difference between Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum in detailed
Here’s a comprehensive comparison between the corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus spongiosum:
- Location and Structure:
- Corpus Cavernosum: Two corpus cavernosum structures within the penis that are located in the dorsal (top) side. They are erectile tissue that is cylindrical composed of spongy and blood vessels called lacunae. The spaces are filled with blood at times of arousal and contribute to penile stiffness and growth.
- Corpus Spongiosum: There is one corpus spongiosum inside the penis. It is located in the ventral (underside) side. It protects and surrounds the urethra or the tube through which semen and urine travel. It is a spongy body but is not a major contributor to penile stiffness.
- Function during Erection:
- Corpus Cavernosum: The main purpose that the Corpus Cavernosum serves to be engorged by blood during sexual stimulation, which leads to the erection from the penis. The stiffness and expansion of this tissue can significantly contribute to the firmness of the erection and size.
- corpus Spongiosum: While the corpus spongiosum is filled with blood during an erection it is still relatively spongy in comparison to corpus cavernosum. Its main function is keeping the urethra clear and clear during erections, permitting fluids to flow without compression.
- Role in Ejaculation and Urination:
- Corpus Cavernosum: The primary function of the corpus cavernosum is to maintain the penile’s rigidity when sexual activity is taking place and is not a direct function in ejaculation or the urination process.
- Corpus Spongiosum: Surrounding the urethra, the corpus is a key component of the ejaculation process. It contracts in a rhythmic manner to push semen into the urethra. It also ensures that the urethra is open both erections and urination. to prevent any obstructions.
- Clinical Significance:
- Corpus Cavernosum: Erectile dysfunction and other conditions may affect the ability of the corpus cavernosum to adequately fill with blood which can lead to problems getting or keeping an erection.
- Corpus Spongiosum: Issues affecting the corpus spongiosum could result in problems related to the urinary function, for instance severe urethral tightures or issues in ejaculation.
Although both the corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus and spongiosum play a vital role in men’s reproductive apparatus, they each have distinct anatomical structures that serve different, but complementary, roles in ensuring a proper reproductive function and sexual functions, as well as erection and the movement of penis fluids.
Comparison chart
Here’s a chart that compares the difference in the corpus cavernosum and the corpus spongiosum:
| Characteristic | Corpus Cavernosum | Corpus Spongiosum |
|---|---|---|
| Location | The Dorsal (top) part of penis | Ventral (underside) side of the penis |
| Number | Two structures present | One structure is present |
| Structure | The erectile cyst has lacunae | The urethra is surrounded by a spongy, fibrous tissue |
| Filling with blood | It fills up significantly when arousal occurs. | It fills, but it remains rather soft |
| Role in Erection | The primary cause of penile rigidity is the penile. | A lesser role is played in penile rigidity |
| Function in Ejaculation | Not directly in any way | Contracts to help semen propulsion |
| Role in Urination | No direct role | Maintains urethral openness during urination |
| Primary Function | Erection | Maintaining and protecting the openness of the urethra |
| Clinical Importance | Erectile dysfunction could alter its functions | Ejaculation issues or Urethral issues |
| Anatomical Position | Dorsally located, separate from the urethra | It encircles and protects the urethra. |
This chart illustrates the most significant distinctions between the corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum, in terms of location as well as their structure, purpose during erection, and role in ejaculation as well as urination and their significance for the male reproductive health.
Similarities between Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum
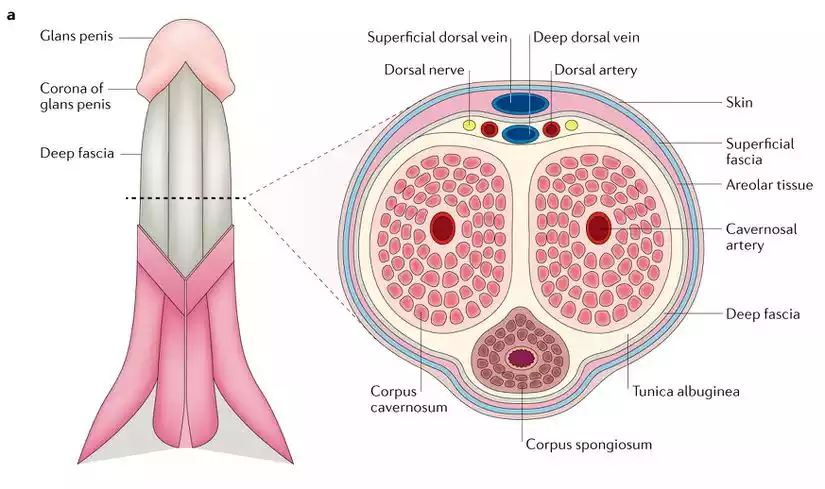
While the corpus cavernosum as well as corpus spongiosum of the reproductive systems of males perform distinct functions, they have some commonalities:
- Erectile Tissue: The corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus spongiosum are erectile tissues that are found inside the penis. They are filled with blood in sexual arousal, which contributes to the physiological processes of getting and maintaining an the erection.
- Vascular Structure: Each tissue has an extensive vascular network which allows them to be filled with blood after stimulation and resulting in an increase in the size and stiffness of the penis when sexual stimulation occurs.
- Blood Flow: Both structures depend on blood flow to fulfill their functions. In the case of sexual stimulation, an increase in blood flow is introduced to these tissues, which causes them to expand, which aids in the expansion and stiffening the penis. The corpus cavernosum has a larger role in the rigidity of the penis.
- The Contribution of HTML0 to Sexual Function: Both the corpus cavernosum and the corpus of spongiosum play a crucial role in male sexual function as well as the mechanics of sexual erection. They have different emphasis. The corpus cavernosum contributes to rigidity as well as expansion of the penis. Meanwhile, the corpus spongiosum helps ensure the urethra’s integrity for the flow of fluids in ejaculation and erection.
- The Supportive Structures: They work in tandem to support the practical features of penis in sexual activities. The corpus cavernosum is responsible for providing the bulk of the rigidity needed to allow for sexual penetration The corpus spongiosum helps support the urethra’s role and helps prevent it from compressing during the process of erection which allows for the flow of urine and semen.
These similarities highlight the synergistic purpose of both structures for creating and maintaining penile erection. They also emphasize their role in the male sexual function as well as reproduction.
Conditions and Disorders Related to Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum
The corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus the spongiosum as integral components in the reproductive process of males may be linked to a range of diseases and conditions:
Corpus Cavernosum-related Conditions:
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): It’s a common condition in which the cavernosum’s corpus does not fill up with blood properly in sexual arousal, which results in difficulty in achieving the desired erection or keeping it. It is caused by vascular issues or neurological issues hormonal imbalances, psychological issues or health issues.
- Privateism: It is described as a painful and prolonged erection that continues beyond sexual stimulation, or lasts more than four hours with no relief. It is often caused by conditions like sickle-cell disease certain drugs trauma, or blood issues. Priapism when left untreated may cause tissue damage and erectile dysfunction.
- Peyronie’s disease: This disorder is caused by the development from fibrous scar tissue inside the cavernosum corpus, resulting in a curvature of the penile and pain when erection occurs and possibly erectile dysfunction.
Corpus Spongiosum-related Conditions:
- Urethral Stricture: It is an enlargement of the urethra caused by scar tissue development. It may be a problem for the corpus of spongiosum, making it difficult to urinate and decreased flow of urine and possibly complications during ejaculation.
- Hypospadias: It is a congenital disorder in which the urethra’s opening is situated on the lower side of the penis rather than at the end. This abnormality affects the corpus spongiosum, and could need surgery to correct it.
- Urethral Diverticulum or Fistula: These are abnormal pouches or openings in the urethra, which may be connected to the corpus spongiosum. They can lead to urinary problems as well as recurring infections. They occasionally require surgery.
- Balanitis and Urethritis: Infections or inflammations of the urethra or the glans penis may indirectly affect the corpus the spongiosum. This can result in discomfort, pain and discomfort when urinating and discharge.
The diagnosis and treatment for these diseases typically involves medical history reviews and physical examination as well as imaging studies. occasionally, surgical procedures or medication specifically designed to treat the root cause. Consultation with a urologist or other healthcare professional who specializes with male reproductive health issues is vital for a precise diagnosis and the proper treatment of these issues associated with the corpus cavernosum and the corpus spongiosum.
How to Maintaining the Health of Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum?
The maintaining of your corpus cavernosum as well as corpus spongiosum is a matter of adopting an active lifestyle and taking care of the factors that improve overall cardiovascular health and well-being.
Here are some guidelines to keep them healthy:
- The Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced, healthy diet that is rich in vegetables, fruits whole grains, whole grains, protein lean, and healthy fats. A diet that is low in saturated fats and cholesterol and processed foods will aid in maintaining cardiovascular health by enhancing in the flow of blood into the erectile tissue.
- Regular Activity: Engage in regular physical exercise to improve cardiovascular health, enhances blood circulation, and helps to improve the function of erectile. You should aim for at minimum 150 mins of aerobic moderate exercise, or at least 75 minutes vigorous activity per week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body weight could cause heart problems which can impact the flow of blood into the corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus spongiosum. Keep a healthy weight by the combination of a balanced diet and a regular workout.
- Stop smoking and limit Alcohol: Smoking damages blood vessels and may affect the erectile system. Drinking excessively can impact sexual function. Avoid or limit both in order to ensure the health of your vascular system.
- Manage chronic health conditions: Conditions like diabetes hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol may affect the flow of blood and nerve function and may affect the health of the erectile tissues. Treat these ailments with medication or lifestyle modifications, as well as regular medical examinations.
- Control Stress: Continuous stress may adversely affect sexual performance. Use techniques to reduce stress, such as yoga, meditation or deep breathing exercises or even hobbies to reduce the stress levels.
- Regularly check-ups are recommended: Regular medical check-ups can aid in identifying and managing any health issues which could impact erectile functioning or urinary health.
- Practice Safe Sexuality: Protecting against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is vital to protect against infections that may be affecting the corpus spongiosum or other female genital structures.
- Avoid trauma or injury: Protect the genital area from injuries or trauma because injury to the penis and the surrounding tissues may affect the function of erectile and urinary health.
- Follow the Medical Advice: If experiencing any problems related to erectile function or urethral health issues, or other issues with your genitals Get prompt medical advice from a specialist in healthcare who specializes in men’s health or urology.
Through focusing on a healthy and balanced lifestyle, taking care of the underlying health issues, and seeking medical attention promptly people can improve healthy corpus cavernosum as well as corpus spongiosum. This will lead to improved overall health and sexual wellbeing.
Importance in male reproductive anatomy
Male reproductive anatomy play a crucial function in the production storage, delivery, and distribution of sperm to reproduce.
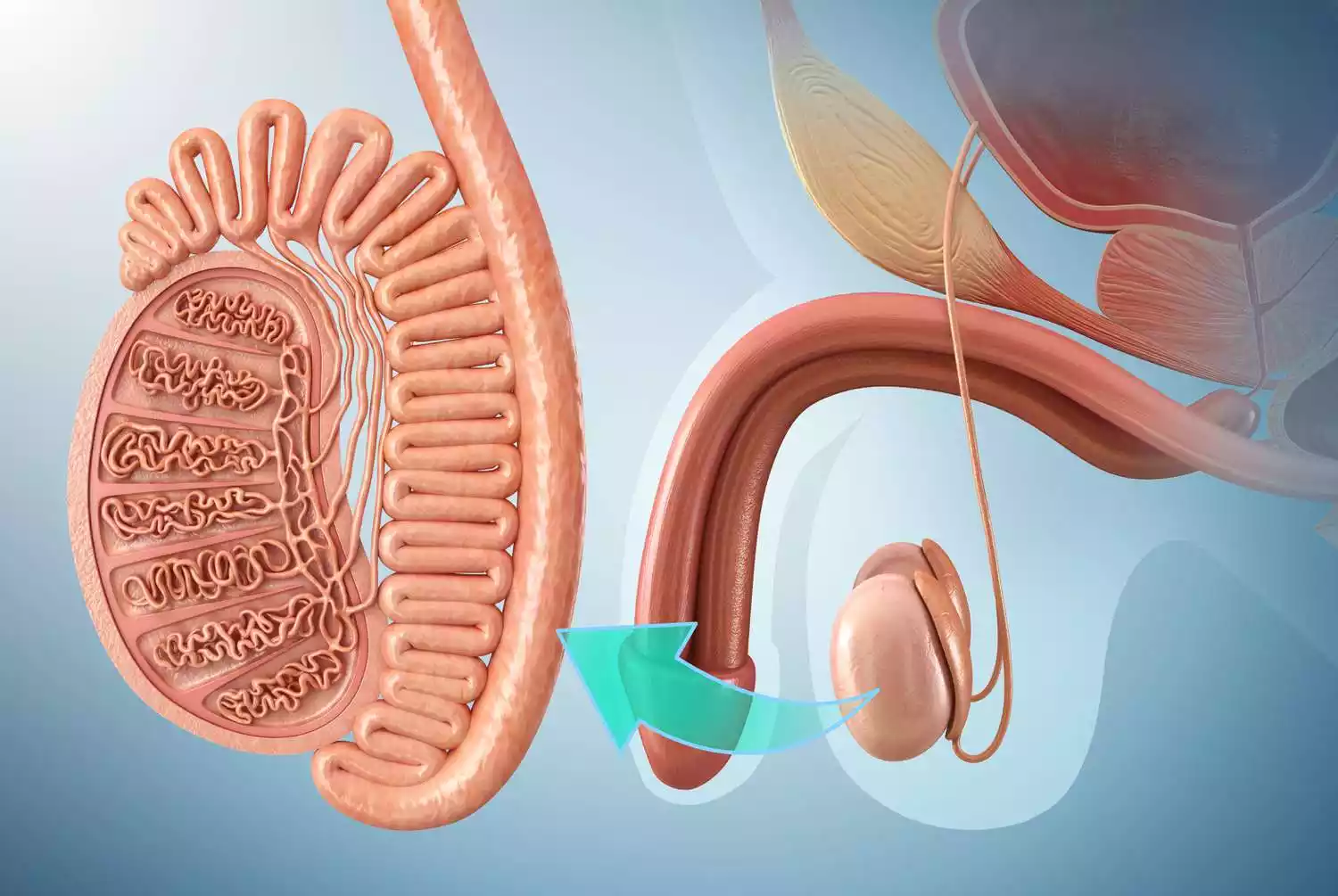
Understanding its importance lies in the following key areas:
- Sperm production: These testes situated in the scrotum create sperm cells by an process known as the spermatogenesis. Sperm cells are vital to fertilize female eggs throughout sexual reproduction.
- Hormone Production: Along with testosterone production, testes also produce hormones, particularly testosterone. Testosterone is essential for growth of the male reproductive tissue as well as secondary sexual characteristics and ensuring reproductive health.
- Ejaculation and Seminal Fluid Production: Together with sperm cell the male reproductive system which includes the accessory glands, such as the seminal vesicles as well as the prostate gland, creates seminal fluid. This fluid nourishes and carries Sperm, making it easier for them to move through ejaculation.
- Sexual Intercourse and Erection: The penis, comprised of erectile tissue such as the corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus spongiosum, allows an erection. Erection happens as these tissues expand with the blood of sexual arousal, permitting penetration during sexual intercourse.
- Urethral Function: The urethra is enclosed by the corpus supragiosum, has a dual purpose within the reproductive organs of males. It is a conduit for urine from the bladder. It it also acts as a conduit for ejaculation. It allows the transfer of semen through the reproductive tract to external.
- Reproduction and Fertility: The male reproductive anatomy comprising vas deferens, testes as well as the ejaculatory tracts and penis, works together to ensure the storage, production as well as release of the sperm that is required to fertilize. This is essential to the continued existence for the entire species.
The understanding of the male reproductive anatomy’s functions, structure and interrelationships is crucial for diagnosing and treating issues with reproductive health including infertility urinary tract infections and sexually transmitted issues. It is also a significant contribution to the discussion of sexual health in general and family planning as well as general health and well-being.
Research and Advancements in Treatment
The field of research in treatments for the corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus the spongiosum has led to advances focused on treating conditions such as erectile dysfunction, urinary issues, and various other problems.
Here are some noteworthy developments:
1. Erectile Dysfunction Treatments:
- Gene Therapy: Researchers are looking into the use of genes to treat the issue of erectile dysfunction. It involves inserting genes into the corpus cavernosum in order to increase blood flow or nerve signaling, which could provide long-term solutions.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Studies are investigating the possibility of using stem cells to heal damaged erectile tissue. Stem cells are injected into the corpus cavernosum have demonstrated potential for repair of tissue and improving the performance of erectile organs.
- Advancements in Medicine: Ongoing research aims to create new drugs that have different mechanisms of action as compared to existing medications, giving greater options to treat Erectile dysfunction. This includes new formulations, specifically targeting the pathways that are that are involved in the penile erection process.
2. Urethral Disorders and Reconstruction:
- The Tissue Engineering: Researchers are investigating techniques for tissue engineering to produce biomimetic substances that can be used to repair or replace damaged tissues of the urethra. This is done by creating scaffolds and cellular structures to restore healthy urethral tissues.
- surgical innovations: Advancements in surgical methods for urethral reconstruction with minimally invasive methods and innovative materials for grafts and repairs that aim to improve outcomes and decrease complications.
3. Combination Therapies and Personalized Medicine:
- Combination Therapy: Research is focused on combining different treatment methods like treatments, medications or treatments that can enhance their efficacy in treating urinary disorders or erectile dysfunction.
- Personalized Medicine: The ability to tailor treatments according to the genetic makeup of an individual as well as lifestyle and particular health issues is a growing area of fascination. The goal of precision medicine is to provide more specific and specific treatments.
4. Telemedicine and Digital Health:
- Platforms for Telemedicine: Advancements in telemedicine allow for better access to specialist medical care for patients suffering from urinary health or sexual issues. Monitoring, remote consultations and even support are now easier to access via the use of digital platforms for health.
The field of research continues to advance by focusing on improving current treatments, developing new treatments as well as expanding our knowledge of the mechanisms that play a role in erectile function as well as urinary health. These advances are likely to lead to better treatment outcomes, and provide many options to those who are affected by ailments related to the corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus spongiosum.
Conclusion
The corpus cavernosum as well as the corpus spongiosum are the two most important parts that make up the male reproductive system. with each having distinct but complementary roles. The corpus cavernosum, which is located behind the penis helps to increase penile rigidity and size when erection is performed, essential to sexual intercourse. In addition, the corpus supragoniosum is located in the ventrally of the urethra ensures its integrity during erection which allows the passage of urine and semen.
Together the erectile tissues help in sexual function by helping with ejaculation and erection and ensuring the urethra’s function. The understanding of their anatomy and function is crucial in addressing issues that affect male sexual health and reproduction, highlighting their importance in maintaining the overall health of male reproductive function.

