Coelom and Pseudocoelom
Coelom and Pseudocoelom serve to describe the function of body cavities within animals. The body cavity is known as coeloms. Coelom as well as pseudocoelom comprise two kinds of body cavities that are found in mammals. They are crucial to the structure and development of internal structures.
Coelom is a genuine body cavity that develops out of mesodermal tissues at the time of embryonic growth. It’s a pore filled with fluid situated between the body’s walls and digestive tract. Coelomates are animals with a coelom, and are various groups like arthropods, annelids, and chordates. The coelom offers comfort, cushioning, and flexibility to organs in the internal that allow the organs to move and work in a way that is independent. This is a characteristic feature of the more sophisticated and advanced living organisms.
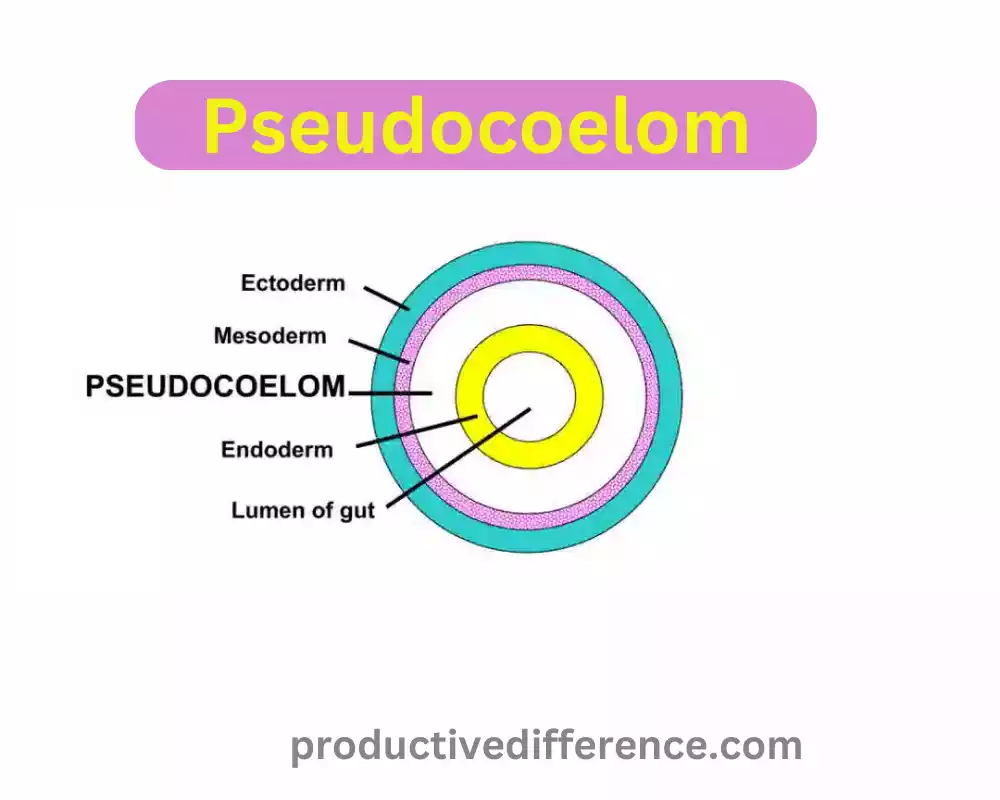
However, it is also a body cavity, which develops out of a mixture of mesodermal and endodermal tissue during the embryonic stage. It’s a space filled with fluid between the body’s wall and the digestive tract but is not completely lined by mesoderm. Pseudocoelomates like nematodes as well as Rotifers, have this kind of cavity in the body. Although it provides some security to organs within the body it does not have the complete protection and flexibility offered by an actual coelom. This makes this a characteristic that is more often observed in smaller species.
Knowing the distinctions between pseudocoelom as well as coelom provides an understanding of the evolutionary diversity of animal species and the adaptations they have made to diverse ecological niches. These cavities in the body have important effects on the complexity and specificity of organ systems in diverse animal species.
Importance of body cavities in organisms
Body cavities play an essential part in the structure, functioning, and development of all living things, especially more complicated creatures. The importance of the body cavity can be seen in the contribution they make to a variety of physiological, anatomical, and evolutionary aspects.
These are the most important points that highlight the importance of the body cavity in living the organisms we live in:
Organ Protection: The body cavities, including the pseudocoelom or coelom create a safe environment for organs within the body. The fluid-filled spaces act as a cushion that protects organs against external impact as well as mechanical impacts.
Organ movement and flexibility: Being able to have a body cavity filled with fluids lets internal organs be mobile and operate independently from one another. This allows for greater effectiveness and flexibility of organ systems and allows greater complexity and coordination of movements.
The space for organ development: The existence of cavities in the body provides ample space for the growth and development of organs within the body. As our organisms develop to become more complicated, the requirement to have organ systems that are specialized develops. Body cavities help in the development of organs and coordination.
Support for Locomotion: in animals that have well-developed body cavities The presence of fluid helps in the process of the ability to move. Examples include peristaltic motions within coelomates, such as earthworms are possible by the coelomic liquid which facilitates muscular contractions.
Hydrostatic Skeletons: In certain organisms like the nematodes (pseudocoelomates) the liquid inside the pseudocoelom serves as a skeleton hydrostatic. It assists in keeping the body’s shape, helps in burrowing and also provides a foundation for the living thing.
Complexity and Adaptability: the existence of body cavities is connected to the increased complexity and adaptability of animal bodies. Organisms with cavities have a wider range of structures as well as specialized roles which allows them to take up various niches in the ecological.
Aspects of Evolutionary Significance: Cavities inside the body is a vital step in the evolution of living creatures. The type and size of cavities in the body can be used to categorize species into distinct classes, which reveal connections and their evolutionary background.
Internal Transport: For some species, the fluids in the body cavity can assist in the transport of gases, nutrients hormones, as well as other waste materials through the body. This facilitates internal communication as well as homeostasis.
In the end, body cavities are essential features that are responsible for the diversity and complexity of living forms in Earth. They are essential to the function, longevity, and survival of living species in their environments.
What is Coelom?
Coelom often referred to as the coelomic cavern, is a cavity in the body that is filled with fluid which is present in all animal species. It’s an essential feature that aids in the evolution of larger organisms.
For animals that have coeloms, the body cavity is covered by mesodermal tissues, that is among the three germ layers of the embryo. As the embryo develops mesoderm creates pouches that expand to create the cavity known as coelomic. The coelomic cavity is a fluid-filled area that lies between the body’s outer wall as well as digestion.
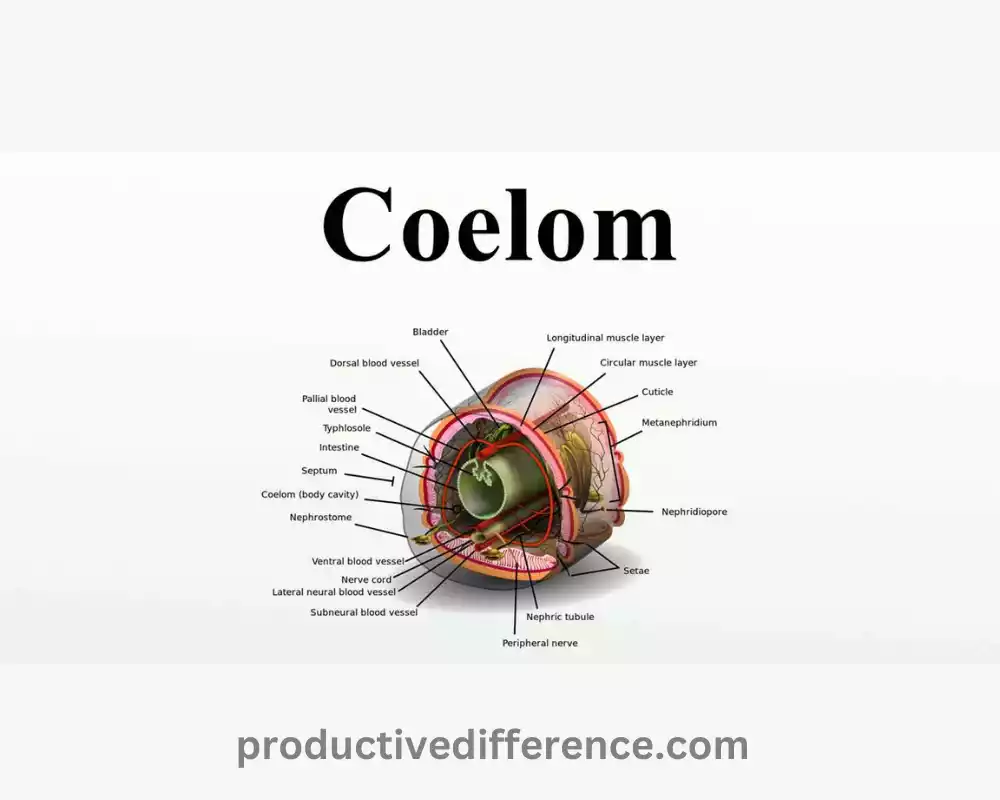
Coelomates, the animals that have the coelom feature, comprise many species, including annelids (e.g. earthworms, earthworms) and arthropods (e.g. crustaceans, insects) as well as mollusks and chordates (e.g. fish, mammals, birds).
Coeloms serve a number of important roles:
Organ movement: The coelom enables organs within the body to operate independent of one another. This flexibility increases the effectiveness of organ systems as well as contributes to the complex nature of our organism.
Circulatory System: in some coelomates, coelomic fluid can play a part in transporting gases, nutrients and other waste substances throughout the body.
The existence of coelom is thought to be an evolutionary breakthrough, which allows the development of greater complexity and adaptability within animal body plans. This is among the primary characteristics utilized to separate animals into distinct categories based on the development of their embryos and their the structure of their bodies.
What is Pseudocoelom?
Pseudocoelom (false body cavity), commonly referred to as the false body cavity in some animal species, refers to an organ filled with fluid in which certain animal species reside. The term is derived from two Greek words “pseudo,” meaning false; and “kilos,” which stands for hollow space or cavity.
In contrast to a real coelom the pseudocoelom does not get lined with mesodermal tissues during the embryonic stage. It is instead formed from mesodermal as well as endodermal tissue. Mesodermal pouches don’t completely cover the body cavity, which leads to the “false” classification.
The pseudocoelom can be found between the wall of the outside body and the digestive tract similar to a real coelom. But its shape and function are different. Pseudocoelomates, species that possess an pseudocoelom include species like Nematodes (roundworms) as well as rotifers and some varieties of flatworms (e.g. the planarians).
The pseudocoelom has a variety of functions:
Partially Organ Support: Although the pseudocoelom can provide assistance and protection for internal organs, it’s not as efficient as an actual coelom, with regard to this.
Limitation in Organ Movement: In comparison with true coelomates Pseudocoelomates exhibit less flexibility and freedom in the movement of their organs.
Transport of Nutrients: In certain pseudocoelomates the fluid in the cavity could help in the distribution of gases, nutrients, and other waste products inside the body.
The appearance of a pseudocoelom can be considered to be an intermediate point during the process of developing the body cavity. It’s among the features used to categorize animals into distinct categories based on their development as well as anatomical traits. Although it isn’t as technologically advanced as the real coelom it still has benefits for some species that allow them to flourish across a variety of ecological niches.
Key difference between Coelom and Pseudocoelom
The coelom’s structure is a crucial element of its purpose and its role in the formation of complicated organisms.
The coelom is a liquid-filled body cavity that is found in a variety of mammals, and it’s shape is distinguished by these important components:
Placement and Location: The coelom is situated between the body’s wall (outermost layer) as well as the digestive tract (innermost layer). It encases the several organs inside, providing each with its own space inside the body.
Mesodermal Lining: The coelom’s interior is completely covered by mesodermal tissues. As embryos develop mesodermal cells create pockets or cavities which expand and then fuse to form the continuous, fluid-filled chamber called the coelom.
Coelomic Fluid Coelomic Fluid: the coelomic cavity is filled with a special fluid that’s known by the name of coelomic fluid. The fluid performs a number of roles, like offering support, serving as a cushion to internal organs and aiding organ mobility.
subdivision and partitioning: In certain animals, coelomic cavities can be divided or partitioned into different compartments through septa or similar forms. The partitioning allows the separation of certain organs and improves the effectiveness and coordination of bodily functions.
Developmental Origins: The coelom is created in the first phases of the development of embryos. The mesoderm develops, and it forms the coelomic cavity. This makes it the most distinctive aspect of coelomates.
Connections to the External environment: The coelom may be linked to external environments via openings such as the nephridia (excretory structure) or the gonoducts (reproductive structure). These openings facilitate the exchange of material between the fluid of coelomic and the outside world.
The shape of the coelom is an essential element in the general functioning and organization of animals that coelomate. It offers support, security as well as flexibility for internal organs that allow for complicated movements as well as the specificization of the organ system. A well-developed coelom is thought to be as an evolutionary breakthrough that has been instrumental in the evolution and the success of different animals.
Structure of Pseudocoelom
The pseudocoelom’s structure is different from the real coelom, and it is a key factor in the growth and function of pseudocoelomate species.
The pseudocoelom is also referred to as the false body cavity features the following main characteristic features:
The location and position of the pseudocoelom: Similar to the coelom, the hypocoelom an additional body cavity that is filled with fluid situated between the body’s exterior wall as well as digestion tract. In contrast to the coelom, the podocoelom is not completely lined with mesodermal tissues.
Mesodermal and Endodermal Parts: The pseudocoelom develops from mesodermal as well as endodermal tissues in the early stages of embryonic development. Contrary to the true coelom made up of mesoderm, the pseudocoelom is composed of both endodermal as well as mesodermal layers.
Pseudocoelomic Fluid: Much like the coelom the pseudocoelomic cavity is also home to the pseudocoelomic fluid. The fluid performs some of similar functions to the coelomic, but it provides only a little help and protection for internal organs.
less developed lining: Unlike the true coelom that is well-developed and continuous in its mesodermal liner, the pseudocoelom could not possess a full mesodermal liner. In addition, the mesodermal as well as endodermal tissues may not completely encompass the entire body cavity.
Simple Structural: Compared to a real coelom structure, that of a pseudocoelom appears to be much simpler. Its mesodermal and endodermal parts and the absence of a mesodermal line can contribute to the structural differences.
Meaning of Evolution: The pseudocoelom is believed to represent an intermediate point in the development of the body cavity. It’s a step in the direction of the more complicated body cavities that are found in coelomates. It has also been a factor in the evolution and diversification of pseudocoelomate living organisms.
Hydrostatic Skeleton: In certain pseudocoelomates like nematodes for instance, the fluid inside the pseudocoelom acts as a skeleton that is hydrostatic. It assists in keeping the body’s shape, helps in burrowing and also provides some assistance to move around.
The overall structure of the pseudocoelom can be described by the mesodermal lining that is partially formed and its link to endodermal tissues, as well as it’s presence as a pseudocoelomic liquid. Although it is less complicated than a coelom that is truly one, the pseudocoelom has benefits to pseudocoelomate animals which allow them to fill different ecological niches as well as perform particular functions within their ecosystems.
Types of Coelom and Pseudocoelom
Types of Coelom:
True Coelom: Trur Coelom also called coelom. This is the most popular kind of coelom that is found in animals that are coelomate. It’s completely lined with mesodermal tissues, which form out of mesodermal pouches in the development of embryos. True coelomates are Annelids (e.g. earthworms) and arthropods (e.g. crustaceans, insects) Mollusks, arthropods, as well as vertebrates (e.g. animals, birds, fish).
Schizocoelom: The type of coelom development involves the breaking or splitting of mesodermal pouches in the embryonic stage. The mesoderm that is split creates the coelomic cavities and leftovers from the splitting process usually become mesodermal tissue of the body’s wall as well as internal organs. Schizocoelom has been observed in many protostome animals like mollusks and arthropods.
Enterocoelom: This kind of coelom development occurs via the invagination and contraction of the archenteron (the primordial gut) in the embryonic stage. The pouches which pinch off from the gut eventually develop into coelomic cavities. Enterocoelom can be seen in the deuterostome of animals, which includes the echinoderms as well as chordates (vertebrates).
Types of Pseudocoelom:
Pseudocoelom: The most popular form of pseudocoelom, as that was previously described, in which the body cavity is formed by combining mesodermal as well as endodermal tissues in the embryonic stage. Some examples of pseudocoelomates are the nematodes (roundworms) as well as rotifers and some flatworms (e.g. the planarians).
Hemocoel: Hemocoel is a different kind of pseudocoelom that is found in a few invertebrates. In contrast to the body’s wall and its digestive tract, it is made up of blood-filled spaces within arthropods, as well as a few other vertebrates. Hemocoel is the main organ cavity and has a vital role to play in the circulation system of these animals.
It is important to remember that even though true coeloms as well as pseudocoeloms have distinct kinds of body cavities, serve a similar purpose to those living in these cavities. The existence of a pseudocoelom, or coelom can have significant consequences regarding the organization, complexity and adaptability of body plans for animals.
The similarity between Coelom and Pseudocoelom
Although Coelom as well as Pseudocoelom are different types of cavities in the body both share a number of similarities in their function and the contribution they make to the living creatures that reside in these cavities.
These are the main similarities that exist between Coelom as well as Pseudocoelom:
Cavity Filled with Fluid: Both Coelom as well as Pseudocoelom are body cavities that contain fluid situated between the body’s wall and the digestive tract in animals. Fluids in these cavities give the body cushioning and support as well as shield internal organs against mechanical traumas.
Organ Movement: Both body cavities permit an element of movement as well as flexible organs within the body. Though true coeloms usually provide more freedom to move however both body cavities are essential to the autonomy of the organs in our body.
Functional significance: the presence of the Coelom, or Pseudocoelom is vital to the life and functionality of organisms with the. Each cavity creates a distinct organ compartment, which helps organ growth and allows for specialization.
Meaning of Evolution: The existence of both Coelom, as well as Pseudocoelom, is regarded to be an important event in the evolution of animal species. They are crucial in the evolution of intricate body cavities. They have also contributed significantly to the evolution of living on Earth.
Ecological Niches: Organisms that are one of Coelom or Pseudocoelom are able to adapt successfully to a variety of ecological niches. Both kinds of body cavities enable species to flourish in varied environments and play a specific role in ecosystems.
Comparative Study The investigation of Coelom and Pseudocoelom as well as their distinctions provides valuable insight on the evolution of diverse animal groups. Recognizing their similarities and differences assists in categorizing animals according to their bodies and their evolutionary background.
Comparison chart
| Aspect | True Coelom | Pseudocoelom |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Derived entirely from mesoderm during embryonic development. | Formed from a combination of mesodermal and endodermal tissues during embryonic development. |
| Lining | Fully lined by mesodermal tissue. | Lacks a complete mesodermal lining; contains both mesodermal and endodermal components. |
| Structural Complexity | More structurally complex and organized. | Relatively simpler in structure compared to true coelom. |
| Examples | Annelids (e.g., earthworms), arthropods (e.g., insects, crustaceans), vertebrates (e.g., mammals, birds, fish), and mollusks. | Nematodes (roundworms), rotifers, certain flatworms (e.g., planarians), and some invertebrates (hemocoel). |
| Organ Protection | Offers effective support and protection to internal organs. | Provides limited support and protection to internal organs. |
| Evolutionary Stage | Represents an advanced evolutionary stage in the development of body cavities. | Considered an intermediate stage between acoelomates and true coelomates in the evolutionary development of body cavities. |
| Functionality | Allows organs to move and function independently, contributing to the complexity of organ systems. | Provides some organ support and facilitates limited organ movement. |
| Hydrostatic Skeleton (in some cases) | Not applicable | In some pseudocoelomates, like nematodes, the fluid within the pseudocoelom functions as a hydrostatic skeleton, aiding in locomotion and support. |
| Examples of Organisms | Earthworms, insects, birds, mammals, etc. | Roundworms, rotifers, planarians, etc. |
Summary
Coelom and pseudocoelom comprise two different types of body cavities that are found in mammals, both with distinctive characteristics and roles.
The coelom is an actual body cavity that is completely lined with mesodermal tissues, which form as embryonic growth progresses. It’s found in many animal species, including arthropods, annelids as well as vertebrates. Coeloms provide assistance, protection and flexibility for internal organs which allows for their own movements and specializedization. This is considered to be an evolutionary advancement that is a factor in the flexibility and complexity of coelomate animals.