Let’s learn about Panthers and leopards and their origin
Panthers and leopards are two majestic big cats that share some similarities but also have distinct characteristics that set them apart. We will delve deep into the differences between panthers and leopards, from physical characteristics, habitat needs, and behavior patterns to the overall appreciation of these incredible animals. By the time this article concludes, you’ll gain a fuller picture of these stunning beasts as well as appreciate their distinctive features and appreciation of what makes each species truly remarkable.
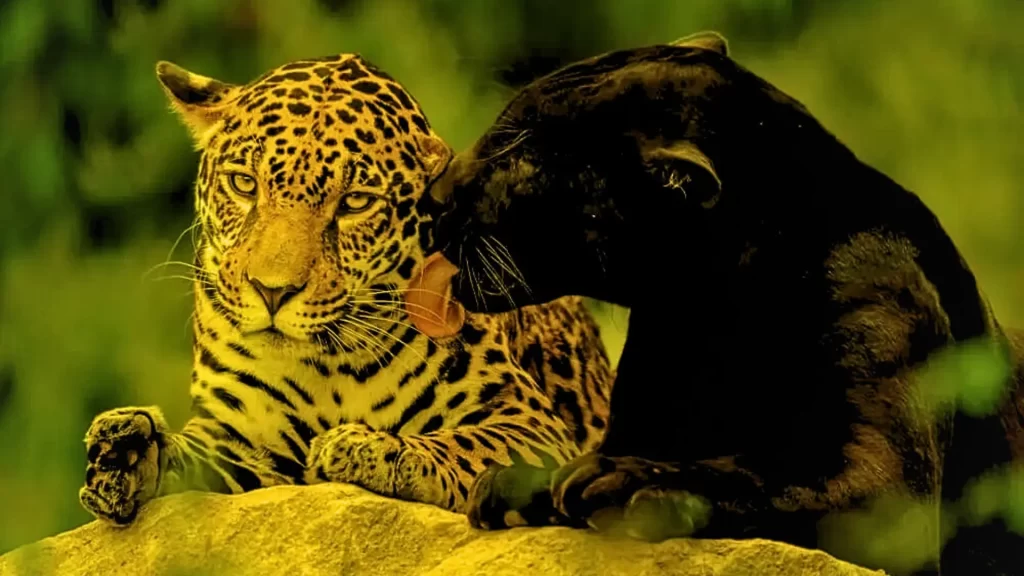

Panthers and leopards both belong to the Felidae family of felines; however, these two feline species differ in terms of appearance. Though often confused as one another, each possesses distinct features which separate it from its relative. While commonly mistaken as synonyms of one another due to overlapping terms between these species names; there are specific traits that distinguish each.
Origin of Panther and Leopard
The panther and the leopard, two majestic big cat species, have fascinating origins that trace back thousands of years. Let’s delve into the evolutionary history of these magnificent creatures and explore their ancient roots.
Felidae Family
Panthers and leopards both belong to the Felidae family of felines, which spans all feline species. Originating millions of years ago and including iconic cats like lions, tigers, and cheetahs among many others – Felidae forms part of the Carnivora order which encompasses carnivorous mammals such as Felidae.
Panther’s Origins
“Panther” is often used to refer to melanistic leopard variants. Panthers possessing melanistic genetic conditions can have completely black coats due to an excess of dark pigmentation that results in characteristic black coloration; underneath their striking black fur lies similar genetic makeup as that found in leopards.
The panther and leopard both can trace their lineage back millions of years to one common feline ancestor that existed millions ago. Through evolution and genetic variations, a melanistic trait emerged, eventually giving rise to panthers as distinct variants of leopards.
Leopard’s Origins
Leopards, with their stunning golden-yellow coats adorned with rosette patterns, have their own unique evolutionary story. The leopard first came on the scene during the Pleistocene period, from 1.5 to 2 million years ago. In Africa and Eurasia, the common ancestor to leopards and panthers inhabited forests and grasslands. As different populations of their ancestors became isolated geographically, they developed distinctive characteristics and adaptations over time. This led to the formation of separate leopard populations.
Geographic Distribution and Migration
The natural habitats of panthers and leopards have influenced their distribution and migration patterns throughout history. Panthers, specifically the Florida panther, have been confined to the dense forests of South and Central America. The isolated populations of panthers in these regions have adapted to the unique environments and resources available to them.
Leopards, on the other hand, have a broader geographic distribution. Leopards can be found throughout Africa – from sub-Saharan regions to the northernmost reaches – while in Asia leopards inhabit various environments like Indian Subcontinent, China, and Southeast Asia.
Climate changes and human interference have altered habitat and migration patterns over the years, impacting genetic diversity as well as distribution for both species.
Conservation and Future
Today, panthers and leopards face numerous conservation challenges. Habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts threaten their survival in the wild. Conservation groups and governments work to protect these amazing creatures, as well as the natural environment. Understanding the origins and evolution of leopards and panthers allows us to appreciate their importance, value, and conservation needs. We can all do our part to ensure their survival as big cat species by supporting conservation initiatives, promoting sustainability practices, and raising awareness.
What is a Leopard?
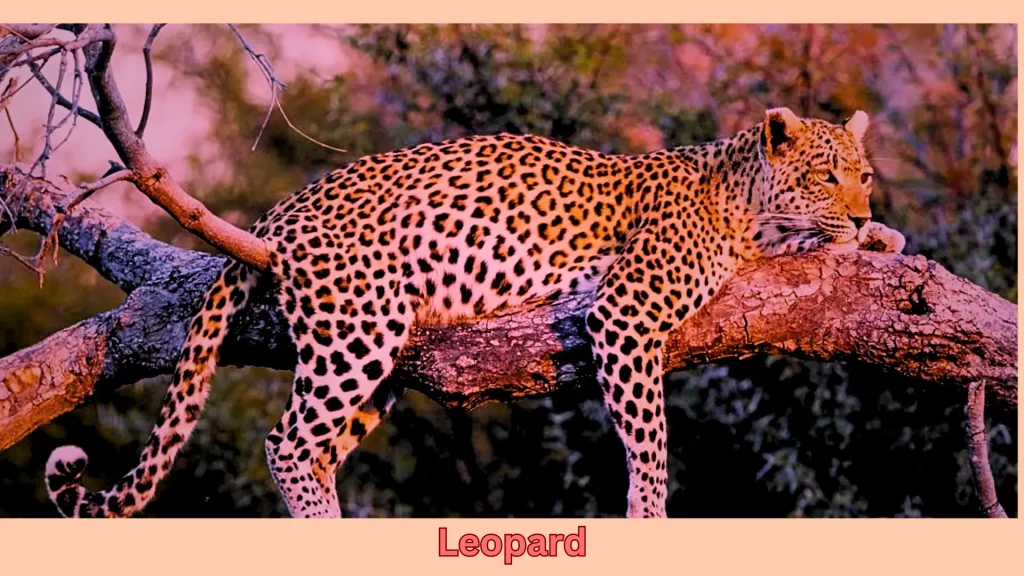

The word leopard was created from combining Greek words for both lions and panthers to refer to one of the smaller members of the big cat family; known for tree-climbing abilities. A leopard’s characteristics include a long body, short but stocky legs, powerful jaws with strong jaw muscles and powerful scapular muscles, a long tail, a large skull, and powerful claws.
Leopard furs have yellowish-brown hues with dark spots. Their maximum length can reach six feet long and weigh up to 100 pounds.
Leopards inhabit rainforests, mountains, deserts, and Savannah tree lines across India, Korea, Malaysia Sri Lanka Siberia Indochina South Africa Central America China Pakistan as their homes.
What is Panther?
The term panther is created from two words that each have a specific meaning; “pan” stands for everything or everything at the same time and “there” refers to prey animals such as cats. Together these form one word with multiple interpretations – panther!
The term panther refers to all members of the big cat family; panthers are known for being master hunters. Characterized by long and slender bodies with long necks and thin shoulders; large eyes with green irises, melanin pigment which gives their fur either black or white colors; shiny spots fur; larger size than its leopard cousin; can weigh up to 350 lbs weighing as many.
Panthers inhabit tropical forests, grasslands, swamplands, marshlands, mountains, and deserts throughout Asia and Africa with significant populations residing in India, Nepal, and China.
Characteristics of Leopard and Panther
Leopards and panthers, both members of the Felidae family, possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. The leopard, with its golden-yellow coat adorned with rosette patterns, is a beautifully camouflaged big cat found in various parts of Africa and Asia. They exhibit remarkable adaptability, thriving in diverse environments such as savannas, rainforests, and mountainous regions. Leopards are agile climbers and skilled swimmers, equipped with sharp senses of hearing and sight. They are adaptable hunters, capable of preying on a wide range of animals, including antelopes, monkeys, birds, and reptiles.
On the other hand, the panther is not a separate species but rather a melanistic variant of the leopard. Panthers have a striking black coat due to an excess of dark pigmentation, but upon close inspection, the characteristic rosette patterns of the leopard can still be discerned. Panthers primarily inhabit the Americas, particularly the dense forests of South and Central America. They are known for their larger size and robust build compared to leopards. Panthers are solitary creatures, preferring to live and hunt alone. They are highly territorial, marking their territories with scent markings and vocalizations.
Both leopards and panthers hold cultural significance in various societies. Panthers, in particular, are revered as powerful and mystical creatures in many indigenous cultures. They symbolize strength, agility, and mystery. Leopards also have cultural importance, with depictions in folklore, mythology, and art.
In terms of conservation status, the Florida panther, a subspecies of the panther, is considered critically endangered. Leopards are considered a vulnerable species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), and they are at risk from threats including habitat loss, poaching, and conflicts with people and other animals. Efforts are being made to protect and conserve both species, emphasizing the importance of preserving their habitats and raising awareness about their significance in maintaining the ecological balance.
Despite their differences, both leopards and panthers captivate us with their beauty, agility, and predatory prowess. Understanding and appreciating their distinct characteristics contribute to the preservation of these magnificent big cats for future generations to admire and cherish.
Main Differences Between Leopard and Panther
- Leopard refers to smaller cats while panther is the general term used for all big cat species – particularly black and white panthers.
- Leopards and panthers are two different species; however, “panther” refers to melanin-containing big cats generally.
- Leopards tend to be smaller in size compared to their fellow members of their family; panthers however are larger than either species.
- Leopards typically weigh 100 pounds; on the other hand, panthers may reach three and half times that of their leopard counterparts with a maximum weight reaching 350.
- Leopard fur is yellowish-brown in color with dark spots; while panther fur can either be shiny black or white.
- Leopards inhabit rainforests while Panthers reside in tropical forests.
- Leopards are well known as tree climbers while Panthers are well renowned for their aggressiveness and keen hunting strategies.
Comparison Table between Leopard and Panther
| Features | Panther | Leopard |
|---|---|---|
| Coat Color | Black (melanistic variant) | Golden-yellow with rosette patterns |
| Size and Weight | Generally larger and more robust | Smaller than panthers |
| Habitat | Primarily found in the Americas | Native to Africa and parts of Asia |
| Distribution | South and Central America | Africa, India, China, Southeast Asia |
| Hunting Techniques | Stalk-and-ambush predators | Adaptable hunters |
| Prey | Deer, wild boar, rodents, smaller mammals | Antelopes, monkeys, birds, reptiles |
| Social Behavior | Solitary | Can exhibit both solitary and social behaviors |
| Cultural Significance | Revered as powerful and mystical creatures | Depictions in folklore, mythology, and art |
| Conservation Status | Critically endangered (Florida panther) | Vulnerable (IUCN classification) |
Similarities between Panther and Leopard
Panthers and leopards share several similarities due to their close evolutionary relationship and belonging to the same genus, Panthera.
Here are some key similarities between panthers and leopards:
- Physical Appearance: Both panthers and leopards have a similar body structure, characterized by a muscular build, a streamlined body, and powerful limbs. They have a large head with sharp, retractable claws, and a long tail that aids in balance and agility.
- Coat Pattern: The coat pattern of both panthers and leopards features rosettes, which are distinctive spots or markings on their fur. While the leopard’s rosettes are more pronounced, the panther’s coat pattern is masked by melanism, resulting in black coloration.
- Carnivorous Diet: Panthers and leopards are both carnivorous predators, feeding primarily on meat. They have similar hunting strategies, relying on stealth, patience, and agility to stalk and ambush their prey.
- Excellent Climbers: Both species are adept climbers, with the ability to ascend trees effortlessly. They often use trees as vantage points for hunting, resting, and escaping from potential threats.
- Nocturnal Behavior: Panthers and leopards are primarily nocturnal animals, being most active during the night. They have adapted to their nocturnal lifestyle, with keen senses and adaptations that aid in hunting and navigating in low-light conditions.
- Solitary Nature: Panthers and leopards are solitary animals, typically preferring to live and hunt alone. They have large home ranges that they mark and defend against intruders of the same species.
- Powerful Predators: Both panthers and leopards are formidable predators and apex predators in their respective ecosystems. They possess exceptional strength, agility, and speed, enabling them to take down prey larger than themselves.
- Adaptability: Panthers and leopards exhibit remarkable adaptability, allowing them to thrive in diverse habitats, including forests, grasslands, and mountains. They have successfully adapted to a range of environments across different continents.
While panthers and leopards share these similarities, it’s important to note that panthers specifically refer to the black melanistic variant of leopards found in certain regions, while leopards encompass the entire species with various coat variations.
Where do Panther and Leopard live?
Panthers and leopards have distinct geographic distributions based on their respective species. Panthers (a black melanistic variant of leopard) can be found primarily throughout South and Central America, inhabiting dense rainforest environments in Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, and Panama as well as Florida (where there exist subspecies such as Florida Panther). Panthers have evolved to adapt to each region’s specific environment as well as available resources and have thus evolved successfully here.
Leopards inhabit various regions across Africa from sub-Saharan regions to North Africa, inhabiting grasslands, forests, mountains, and deserts across all environments imaginable. Furthermore, leopards also exist as populations in parts of Asia such as India China Sri Lanka Malaysia Indonesia as well.
The adaptable nature of leopards allows them to thrive in different environments, ranging from savannas and woodlands to high-altitude regions. This wide distribution across Africa and Asia showcases the remarkable adaptability of the leopard species.
These regions can differ depending on factors like climate, vegetation, and prey availability; panthers and leopards’ geographic distribution reflects their evolutionary history and adaptations to diverse ecosystems – further emphasizing their remarkable survival abilities.
Food habit of Panther and Leopard
Panthers and leopards, both being big cat species, have similar food habits as carnivorous predators. They are skilled hunters with adaptations that enable them to capture and consume a variety of prey.
Leopards have a diverse diet and are known for their opportunistic hunting behavior. They are adaptable hunters that can thrive in different habitats and feed on a wide range of animals. Leopards hunt antelopes, deer, wild boars, monkeys, birds, reptiles, and smaller mammals for food, depending on camouflage to sneak up behind prey before unleashing powerful attacks to kill it quickly. Leopards are adept hunters who employ stealth as part of their hunting style before quickly attacking.
Panthers, on the other hand, which are a melanistic variant of leopards, share the same food habits as their non-melanistic counterparts. They also prey upon animals similar to those hunted by leopards. Panthers primarily feed on deer, wild boar, rodents, smaller mammals, and other suitable prey species found in their respective habitats. Despite their black coat, which provides them with camouflage advantages in certain environments, panthers rely on their keen senses, agility, and strength to capture their prey.
Panthers and leopards both serve as top predators within their ecosystems, meaning that they occupy the pinnacle of food chains. Both predator species possess exquisite hunting techniques tailored for successful predation – they possess powerful jaws with sharp teeth to ambush prey before using retractable claws to complete the kill.
Notable among panthers and leopards as carnivorous predators are their tendency to feed on prey that is available within their ecosystem, regardless of geographical distribution and availability of prey species. Though their diet varies based on these variables, their overall eating behavior demonstrates their important ecological roles as carnivores in maintaining balance within these respective ecologies.
The difference in hunting style between Panther and Leopard
Panthers and leopards, despite sharing similarities in their hunting habits as members of the same genus, exhibit some differences in their hunting styles.
Leopards are known for their remarkable adaptability and versatility when it comes to hunting. They employ a stalk-and-ambush strategy, which involves stealthily approaching their prey, using their excellent camouflage to remain undetected. Leopards carefully observe their environment, patiently waiting for an opportunity to strike at unsuspecting prey. Their powerful muscular bodies allow them to quickly chase after and catch animals using both speed, agility, and brute force to capture prey quickly and kill it with great efficiency.
Panthers, being a melanistic variant of leopards, share the same hunting techniques and rely on the stalk-and-ambush approach. However, due to their predominantly black coat, panthers may have an added advantage in certain environments where their dark coloration provides them with enhanced camouflage. This enables them to blend seamlessly into the shadows, making them less visible to their prey. Panthers utilize their stealth and agility to silently approach their target, ensuring a successful ambush.
Both panthers and leopards possess exceptional senses, including acute hearing, sharp vision, and a strong sense of smell. These sensory abilities aid them in detecting and locating potential prey. They are opportunistic hunters, adapting their hunting strategies based on the availability and behavior of their prey in their respective habitats.
It’s worth noting that individual hunting styles can also vary within populations of both panthers and leopards, influenced by factors such as the environment, prey abundance, and learned behaviors. The fundamental stalking and ambushing techniques remain characteristic of their hunting styles.
Understanding the differences in hunting styles between panthers and leopards provides insights into their unique adaptations and behaviors, showcasing their remarkable skills as efficient predators in their respective ecosystems.
What is the main cause of the vanishing Panther and Leopard?
The main cause behind the vanishing populations of panthers and leopards is a combination of human-related factors that have significantly impacted their survival.
These factors include:
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: The conversion of natural habitats into agricultural lands, urban areas, and infrastructure development has resulted in the loss and fragmentation of the habitats where panthers and leopards reside. Deforestation, land clearing, and expansion of human settlements have greatly reduced their available living spaces, limiting their access to resources and increasing the likelihood of human-wildlife conflicts.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade: Both panthers and leopards are targeted by illegal wildlife trade for their skins, bones, and other body parts, driven by demand for traditional medicine, exotic fashion, and trophy hunting. This ruthless trade has severely impacted their populations, pushing them to the brink of extinction.
- Poaching and Hunting: Poaching for their pelts, body parts, and trophies remains a significant threat to panthers and leopards. Despite international regulations and protective measures, these big cats are still targeted by hunters seeking their valuable and exotic body parts.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: As human populations expand and encroach upon natural habitats, conflicts between humans and panthers or leopards escalate. Instances of predation on livestock and, in rare cases, attacks on humans lead to retaliatory killings and negative perceptions towards these majestic cats.
- Lack of Awareness and Conservation Efforts: Limited awareness and inadequate conservation measures contribute to the decline of panther and leopard populations. Insufficient resources, funding, and capacity to effectively protect and manage their habitats exacerbate the challenges they face.
Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach that involves habitat conservation, strengthened law enforcement against illegal wildlife trade, community engagement, public awareness campaigns, and international collaboration. By addressing the root causes of their decline and implementing comprehensive conservation strategies, we can strive to reverse the trend and ensure a sustainable future for panthers and leopards in the wild.
How we can preserve Panther and Leopard

Preserving panthers and leopards requires concerted efforts and a combination of conservation strategies.
Here are some key approaches to help preserve these magnificent big cat species:
- Protected Areas and Habitat Conservation: Establishing and effectively managing protected areas, national parks, and wildlife reserves that encompass their habitats is crucial. These areas should be adequately protected from encroachment, habitat loss, and degradation.
- Anti-Poaching Measures: Implement strong anti-poaching measures to combat illegal hunting and trade. This includes strengthening law enforcement, increasing patrols, utilizing technology such as camera traps, and imposing strict penalties for poaching activities.
- Promote Sustainable Land Use: Encourage sustainable land-use practices that minimize habitat destruction and fragmentation. This involves supporting initiatives such as reforestation, promoting sustainable agriculture, and reducing human-wildlife conflicts through measures like predator-proof enclosures for livestock.
- Community Involvement: Engage local communities living in proximity to panther and leopard habitats. Promote awareness, provide alternative livelihood options, involve them in conservation initiatives, and emphasize the ecological importance of these species.
- Education and Awareness: Raise public awareness through educational programs, outreach campaigns, and media platforms. Educate communities, schools, and the general public about the significance of panthers and leopards in maintaining healthy ecosystems and the need for their conservation.
- Research and Monitoring: Conduct scientific research, monitoring, and population surveys to gather crucial data on panther and leopard populations, behavior, and threats. This information informs conservation strategies and helps evaluate the effectiveness of implemented measures.
- International Cooperation: Foster collaboration between countries, organizations, and stakeholders to share knowledge, resources, and best practices. Collaborative efforts can strengthen conservation initiatives, promote information exchange, and facilitate coordinated actions across borders.
- Policy and Legislation: Advocate for policies and legislation that safeguard panthers and leopards against habitat destruction, illegal trade, and hunting. Support international agreements like CITES to regulate and control the trade of these endangered species.
- Conservation Breeding Programs: Establish and support conservation breeding programs aimed at maintaining healthy captive populations and potential reintroductions into the wild, if suitable habitats are available.
By implementing these measures collectively and continuously, we can contribute to the preservation and long-term survival of panthers and leopards, ensuring that these magnificent big cats continue to thrive in their natural habitats for future generations to admire and cherish.
Final words
Panthers and leopards are magnificent big cat species that share both similarities and distinct characteristics. They belong to the same genus, Panthera, and possess common traits such as a muscular build, a coat pattern featuring rosettes, a carnivorous diet, and excellent climbing abilities. Both panthers and leopards are nocturnal, solitary predators, demonstrating remarkable strength, agility, and adaptability.
The key distinction lies in the coat coloration, with panthers being a melanistic variant of leopards, exhibiting a black coat due to an excess of dark pigmentation. This striking feature sets them apart visually, while the underlying genetic makeup remains similar.